Installation (NEW)
The EnMAP-Box is a plugin for QGIS and requires additional python packages that need to be installed independent from QGIS.
QGIS Installation on Windows
On a Windows system you have multiple options to install QGIS.
Option A: Install QGIS via the official Standalone/OSGeo4W Installer
1. Install QGIS
Install either the current QGIS Long Term Release (LTR) or the current QGIS Latest Release (LR) to run the latest EnMAP-Box. You can get the QGIS Standalone Installer here. For beginners, we recommend using the standalone installers. More advanced QGIS users can use OSGeo4W installer.
In case you already have the current QGIS LTR or LR version installed, you can skip this step.
In case you have an outdated QGIS version, make sure to install a current version.
2. Install Python Dependencies
Close QGIS, if it is open.
Open the OSGeo4W Shell from the start menu.
Install Python dependencies by executing:
pip install --upgrade --user -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EnMAP-Box/enmap-box/main/.env/osgeo4w/requirements_osgeo4w.txt
Open QGIS from the start menu.
Option B: Install QGIS via the Mambaforge Package Manager
1. Install Miniforge
It is recommended to use Miniforge, a minimal installer for Conda specific to conda-forge. You can get the Miniforge Windows Installer here.
2. Install QGIS and Python Dependencies
Open the Miniforge Prompt from the start menu.
Install QGIS LTR and EnMAP-Box Python dependencies into a new “enmapbox” environment:
mamba env create -n enmapbox -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EnMAP-Box/enmap-box/main/.env/conda/enmapbox_full_longterm.yml
Activate the “enmapbox” environment and open QGIS by executing:
activate enmapbox qgis
QGIS Installation on Linux (Ubuntu)
The following instructions were written for and tested on Ubuntu (22.04 & 23.10). They should also work for other Debian-based distributions.
Option A: Install QGIS via the official repository
1. Install QGIS
Install QGIS as described here https://www.qgis.org/de/site/forusers/alldownloads.html#debian-ubuntu
2. Install Python Dependencies
Open the Terminal (Ctrl + Alt + T).
Make sure the following packages are installed using the system package manager:
sudo apt install python3-pip python3-venv pyqt5-dev-tools(optional) for some EnMAP-Box tools you may also need the following packages:
sudo apt install python3-h5py python3-pyqt5.qtopengl python3-netcdf4Open QGIS and the QGIS Python Console (Ctrl + Alt + P). Type the following and confirm with enter:
import sys; sys.executable
It shows the path of the python executable QGIS is using, usually
/usr/bin/python3. It should be the same path as the commandwhich python3executed in the Terminal returns! Close QGIS.Create a virtual python environment in a directory of your choice (e.g.
~/.virtualenvs/enmapbox):python3 -m venv --upgrade-deps --system-site-packages ~/.virtualenvs/enmapboxActivate the environment:
source ~/.virtualenvs/enmapbox/bin/activateNow you should see the environment name in brackets at the beginning of your prompt, e.g.
(enmapbox).Install missing python dependencies with pip inside the virtual environment:
python3 -m pip install -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EnMAP-Box/enmap-box/main/.env/linux/requirements_ubuntu.txtStart QGIS (from the activated environment, see 6.):
qgis
Hint
You can add a shortcut to your applications menu, so you do not have to open a Terminal and type the above mentioned commands (6. & 8.) everytime you want to start QGIS with the EnMAP-Box environment:
Create the file ~/.local/share/applications/enmapbox.desktop with the following content (if you used another installation path
in the instructions above change accordingly):
[Desktop Entry]
Name=QGIS (EnMAP-Box)
Exec=/bin/bash -c "source ~/.virtualenvs/enmapbox/bin/activate && qgis %F"
Terminal=false
Icon=qgis
Type=Application
Categories=Education;Science;Geography;
Option B: Install QGIS via conda/mamba
1. Install Micromamba
It is recommended to use Micromamba, a minimal installer for conda/mamba.
You can get Micromamba here. You may
of course also use conda, just swap micromamba with conda in the instructions below.
2. Install QGIS and Python Dependencies
Open the Terminal, and install QGIS LTR and EnMAP-Box Python dependencies into a new “enmapbox” environment:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EnMAP-Box/enmap-box/main/.env/conda/enmapbox_full_longterm.yml micromamba env create -n enmapbox -f ./enmapbox_full_longterm.yml rm -v ./enmapbox_full_longterm.yml
Note
There are multiple environment files available, depending on whether you want to install the latest qgis version or the long-term release.
Activate the created “enmapbox” environment and open QGIS by executing:
micromamba activate enmapbox qgis
QGIS Installation on MacOS
todo @jakimow
EnMAP-Box Plugin Installation
In QGIS go to
In the search bar enter
enmapNow the EnMAP-Box should be listed in the plugin list:
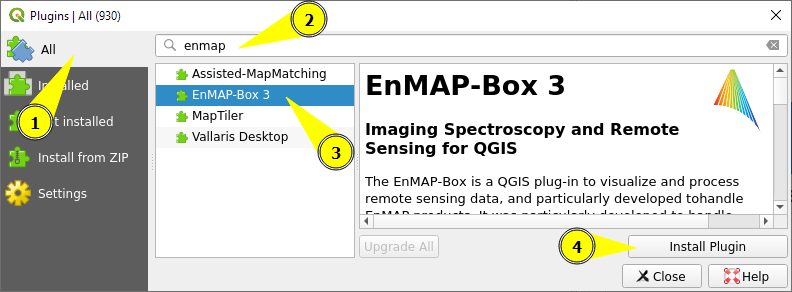
Select it and click Install plugin (or Upgrade in case you update to a new version)
The following dialog might pop up afterwards:
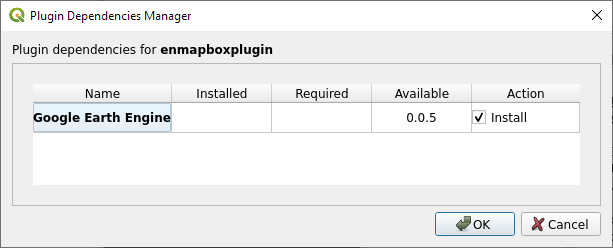
Depending on whether you want to use the GEE Time Series Explorer check
 or uncheck
or uncheck  the checkbox
and confirm with OK
the checkbox
and confirm with OK(Optional): You can download a demo dataset via
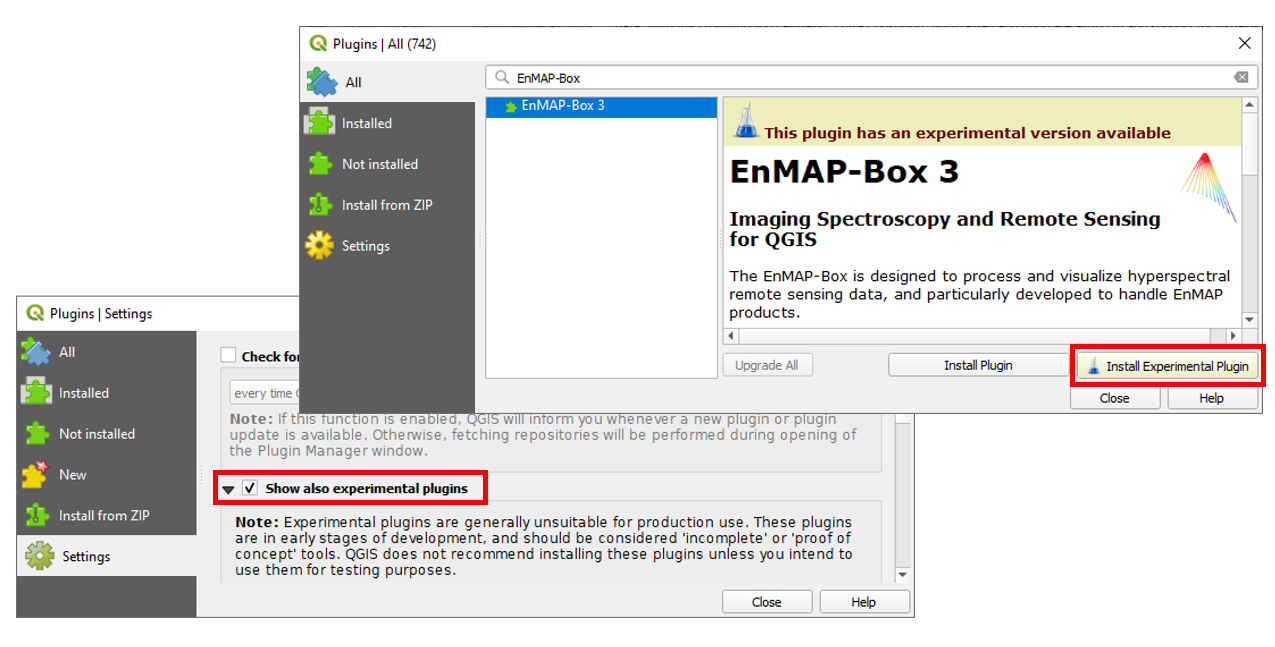
Experimental version
It is also possible to install the most recent develop version of the EnMAP-Box. To do so, make sure that the option
 Show also experimental plugins is activated in the plugin manager settings. Once activated, there is an additional button
Install Experimental Plugin in the plugin manager.
Show also experimental plugins is activated in the plugin manager settings. Once activated, there is an additional button
Install Experimental Plugin in the plugin manager.
Warning
As the experimental tag suggests, this version comes with the newest features and developments, but might also be prone to bugs and crashes.