The GUI¶
Overview of the EnMAP-Box
Toolbar¶
In the toolbar you can find the most common tasks. See table below for information on different buttons and their functionality.
It is possible to enable and disable the different tools: Right-click
on the toolbar and check or uncheck the desired toolbar.
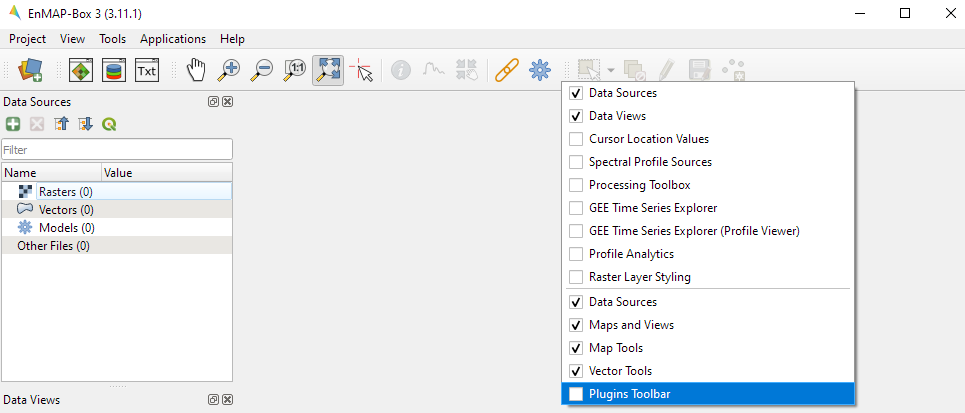
Enable and disable different toolbars
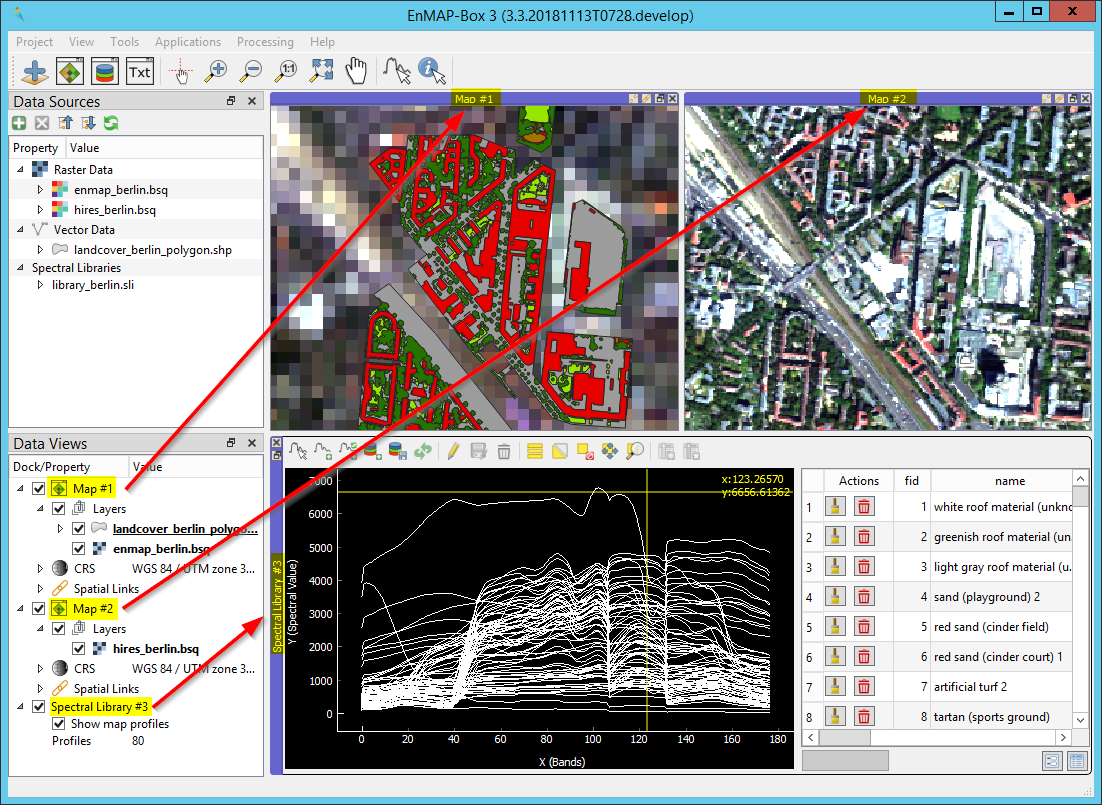
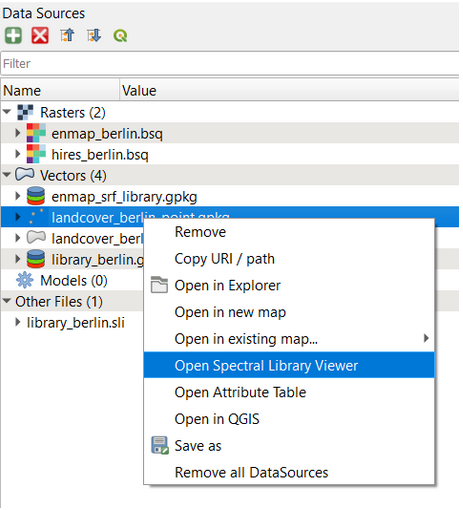
Data Sources¶
| Button | Button Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Adds a data source | Here you can add data from different sources, e.g. raster and vector |
Maps and Views¶
Map Tools¶
Vector Tools¶
Earth Observation for QGIS (EO4Q)¶
| Button | Button Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GEE Time Series Explorer | Opens the GEE Time Series Explorer in a new view. | |
| Location Browser | Use point location or geometry formats to navigate to a specific location or send a request to the Nominatim Geocoding service of OpenStreetMap. | |
| Profile Analytics | Opens the Profile Analytics in a new view. | |
| Raster Band Stacking | Stack different raster bands individually. | |
| Sensor Product Import | Import different sensor products by drag & drop. |
Panels¶
Data Sources¶
The Data Sources panel lists the data in your current project, comparable to the Layers panel in QGIS. The following data types and their corresponding metadata are available:
-
File size: Metadata on resolution and extent of the raster
CRS: Shows Coordinate Reference System (CRS) information
Bands: Information on overall number of bands as well as band-wise metadata such as name, class or wavelength (if available)
Note
Depending on the type, raster layers will be listed with different icons:
for default raster layers (continuous value range)
for mask raster layers
for classification raster layers
Also see section on data types for further information.
-
- File size: Shows the file size and extent of the vector layer
- CRS: Shows Coordinate Reference System (CRS) information
- Features: Information on number of features and geometry types
- Fields: Attribute information, number of fields as well as field names and corresponding datatype
-
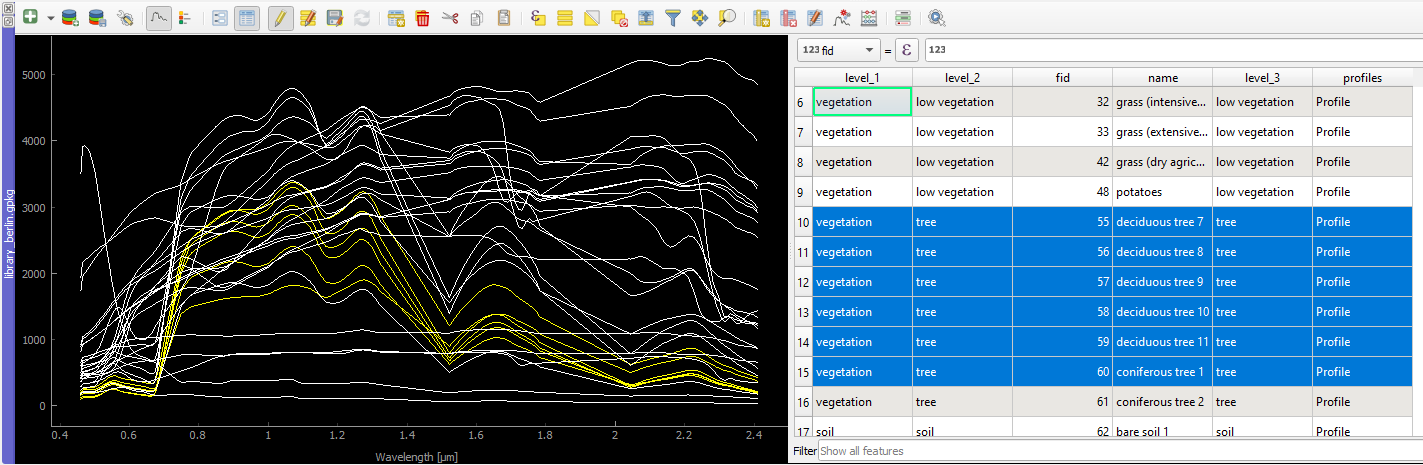
- File size: Size of the file on hard disk
- Profiles: Shows the number of spectra in the library
Buttons of the Data Sources panel:
Tip
- If you want to remove all layers at once, right-click
in the Data Sources panel and and select Remove all DataSources
- The EnMAP-Box also supports Tile-/Web Map Services (e.g. Google Satellite or OpenStreetMap) as a raster layer. Just add them to
your QGIS project as you normally would, and then click the
Synchronize Data Sources with QGIS button. Now they should appear in the data source panel and can be added to a Map View.
Data Views¶
The Data Views panel organizes the different windows and their content. You may change the name of a Window by double-clicking onto the name in the list.
Buttons of the Data Views panel:
Organization of the Data Views panel:
Example of how different window types and their contents are organized in the Data Views panel. In this case there are two Map Views and one Spectral Library View in the project.
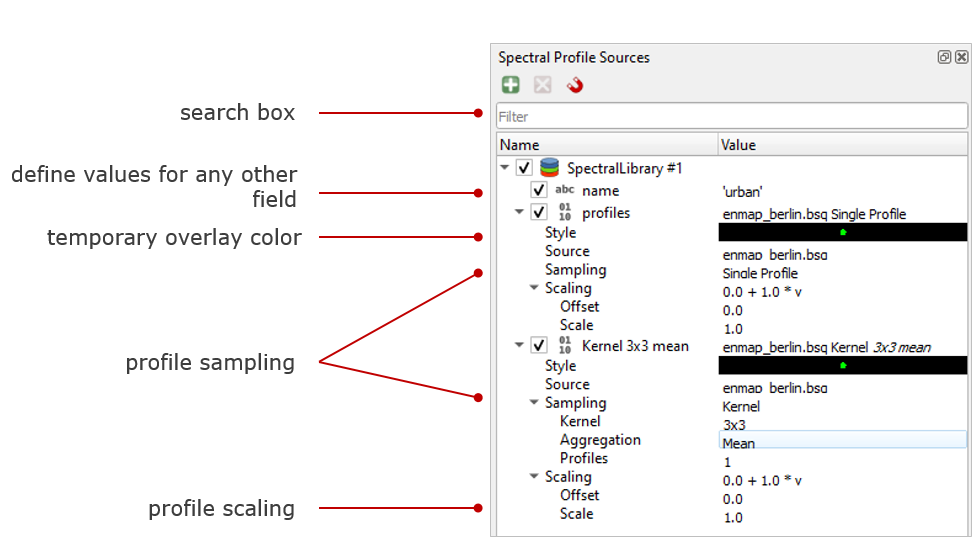
Spectral Profile Sources¶
This menu manages the connection between raster sources and spectral library windows.
When collecting profiles, the Identify tool selects profiles from the top-most raster layer by default. The Profile Source panel allows to change this behaviour
and to control:
the profile source, i.e., the raster layer to collect profiles from,
the style how they appear in the profile plot as profile candidate,
the sampling method, for example to aggregate multiple pixel into a single profile first,
the scaling of profile value.
Overview of the Spectral Profile Sources Window with two labeled spectra and main functionalities
Buttons of the Profile Sources
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
| add a new profile source entry | |
| remove selected entries |
- Profiles
- Define the input data from where to take the spectral information from.
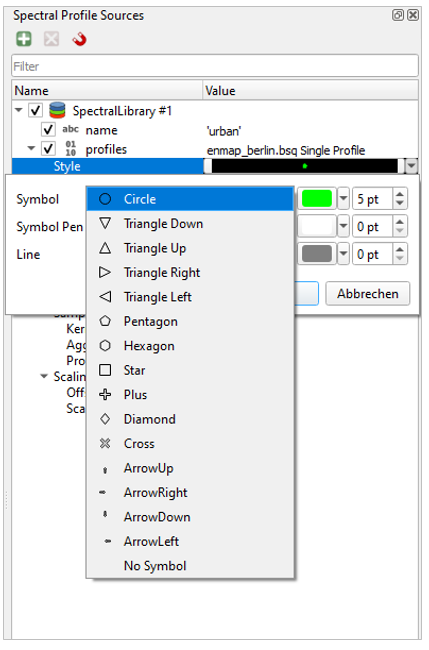
- Style
Change style of displayed spectra, i.e. symbol and color
- Source
- Specify a source raster dataset
- Double-clicking in the cell will open up a dropdown menu where you can select from all loaded raster datasets.
- Sampling
- Select Single Profile or Kernel by double-clicking into the cell.
- Scaling
- Choose how spectra are sampled.
- Define the scaling factors by setting the Offset and Scale value.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| SingleProfile | Extracts the spectral signature of the pixel at the selected location |
| Sample3x3 | Extracts spectral signatures of the pixel at the selected location and its adjacent pixels in a 3x3 neighborhood. |
| Sample5x5 | Extracts spectral signatures of the pixel at the selected location and its adjacent pixels in a 5x5 neighborhood. |
| Sample3x3Mean | Extracts the mean spectral signature of the pixel at the selected location and its adjacent pixels in a 3x3 neighborhood. |
| Sample5x5Mean | Extracts the mean spectral signature of the pixel at the selected location and its adjacent pixels in a 5x5 neighborhood. |
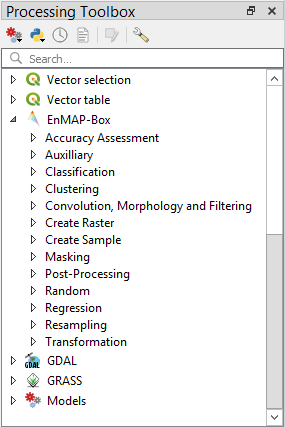
Processing Toolbox¶
The processing toolbox is basically the same panel as in QGIS. Here you can find all EnMAP-Box processing algorithms
listed under EnMAP-Box. In case it is closed/not visible you can open it by clicking the
button in the menubar or .
See QGIS Documentation - The toolbox for further information.
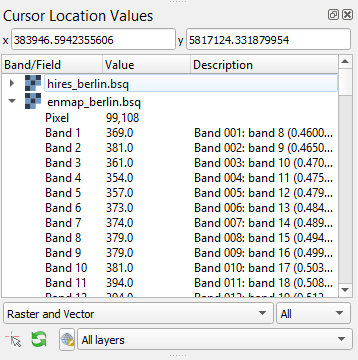
Cursor Location Values¶
This tools lets you inspect the values of a layer or multiple layers at the location where you click in the map view. To select a location (e.g. pixel or feature)
use the Select Cursor Location button together with the
Identify cursor location value option activated and click somewhere in the map view.
The Cursor Location Value panel should open automatically and list the information for a selected location. The layers will be listed in the order they appear in the Map View. In case you do not see the panel, you can open it via .
By default, raster layer information will only be shown for the bands which are mapped to RGB. If you want to view all bands, change the Visible setting to All (right dropdown menu). Also, the first information is always the pixel coordinate (column, row).
You can select whether location information should be gathered for All layers or only the Top layer. You can further define whether you want to consider Raster and Vector layers, or Vector only and Raster only, respectively.
Coordinates of the selected location are shown in the x and y fields. You may change the coordinate system of the displayed coordinates via the
Select CRS button (e.g. for switching to lat/long coordinates).
Views¶
Map View¶
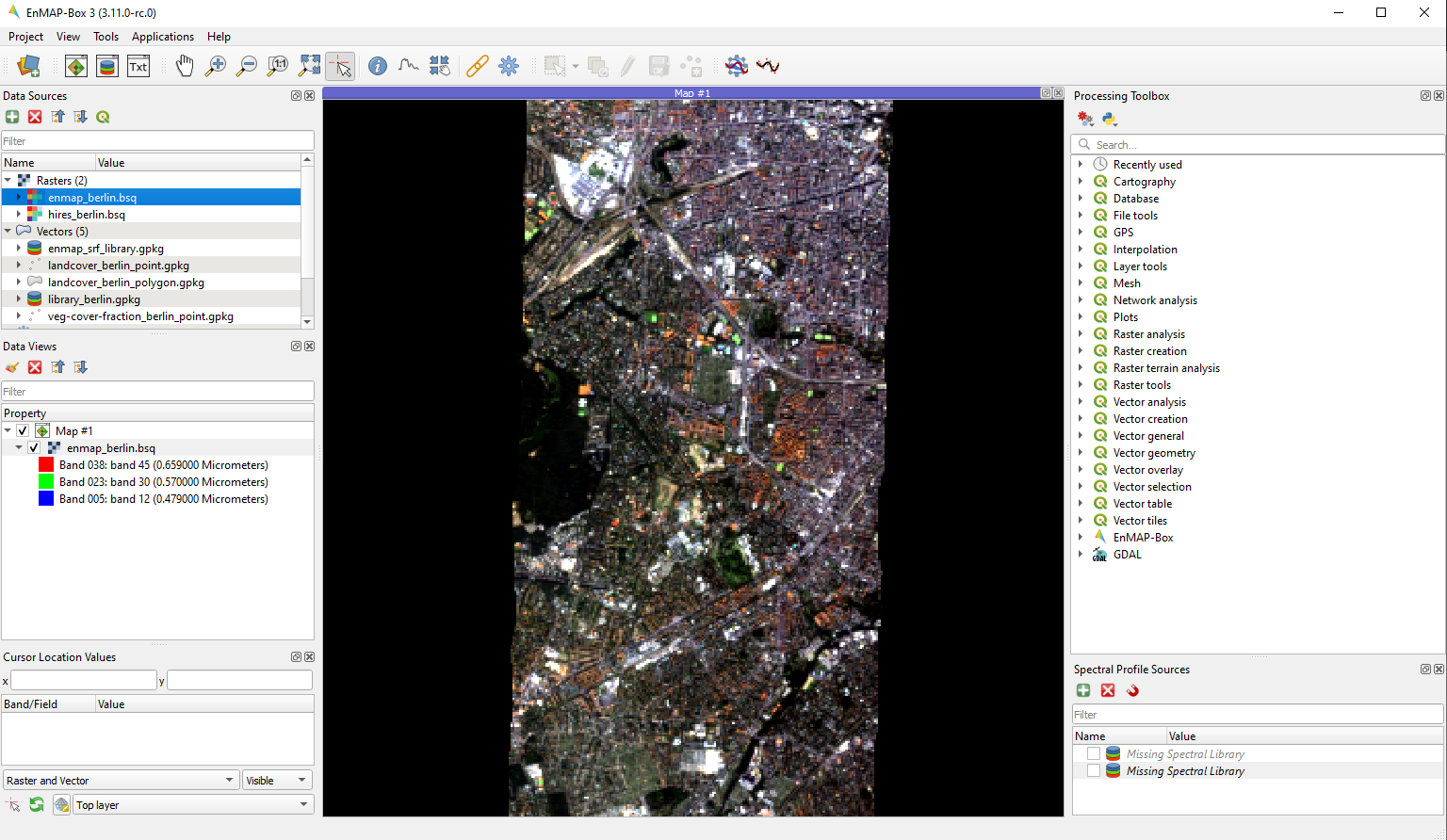
The map view allows you to visualize raster and vector data. It is interactive, which means you can move the content or zoom in/out.
In order to add a new Map View click the
Open a Map View button. Once you added a Map View, it will be listed in the
Data Viewspanel.Add layers by either drag-and-dropping them into the Map View (from the Data Sources list) or right-click
onto the layer
You can also directly create a new Map View and open a layer by right-clicking
the layer
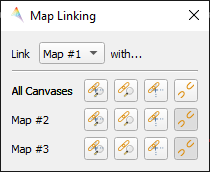
Linking¶
You can link multiple Map View with each other, so that the contents are synchronized. The following options are available:
In order to link Map View, go to in the menu bar, which will open the following dialog:
Here you can specify the above mentioned link options between the Map Views. You may either specify linkages between pairs
or link all canvases at once (the All Canvases option is only specifiable when the number of Map Views is > 2). Remove
created links by clicking .
Demonstration of linking two Map Views
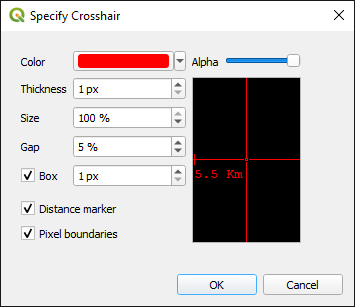
Crosshair¶
Spectral Library View¶
The Spectral Library Window offers (almost) the same tools like the standard QGIS attribute table. In addition, it provides views and features specifically to visualize and manage spectral profiles. It directly interacts with the Map View(s), which means spectra can be directly collected from an image. Furthermore, external libraries (e.g. ENVI Spectral Library) can be imported.
Add a new spectral library view by using the Add Spectral Library Window button in the toolbar or open a new window from the menu .
Overview of the Spectral Library view with several collected and labeled spectra and main tools
Buttons of the Spectral Library Window
Collect profiles¶
Make sure to enable the
and
button in the menu bar and open a raster from which you want to collect spectra in a new Map View.
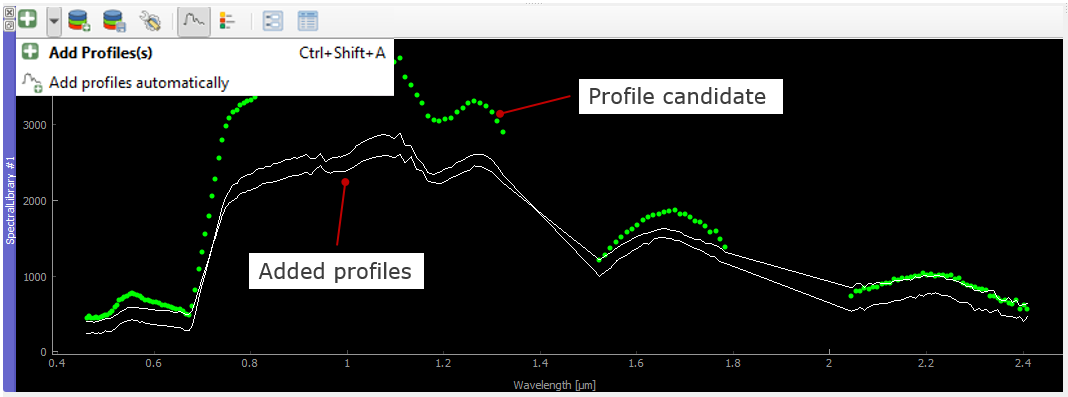
Click on a desired pixel position in the opened raster image and a new Spectral Library window opens with the spectral profile of the respective pixel.
Profiles obtained from pixel positions are considered as current or temporary profile candidates. The last profile candidate will be replaced by a new one each time you click on a new pixel position.
Click on Add Profile(s)
to keep the candidate profile in the spectral library. Activate Add profiles automatically
to collect multiple profiles and display them all in the same spectral library.
As an alternative to the mouse you can also identify and select pixel profiles using the shortcuts to change, select and add pixel profiles to the Spectral Library.
First activate the crosshair for the respective image. Click with the right mouse button in the image. Select Crosshair > Pixel Grid > desired raster image.
Now you should see a red square around your pixel and a red dot indicating the position of the pixel profile.

To identify, select and add a pixel profile, use the following key combinations:
| Shortcut | Action |
|---|---|
| ←/↑/↓/→ | Move the map |
| Ctrl + ←/↑/↓/→ | Select next pixel in arrow direction |
| Ctrl + S | Add the selected pixel profile candidate |
Add profiles from another raster image
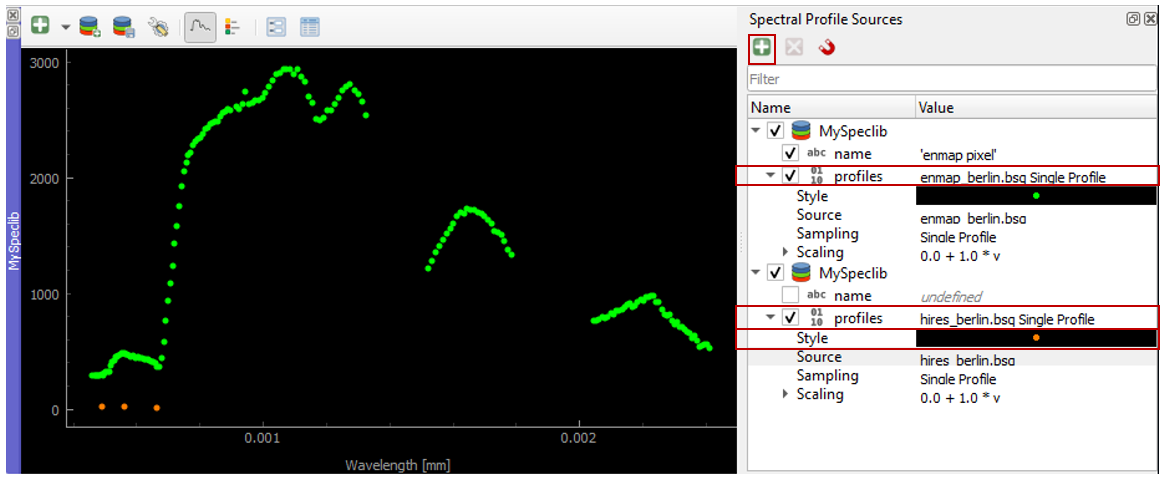
Sometimes, you want to compare spectral profiles from different raster sources. The Spectral Profile Source panel allows you to change the default settings of the Identify tool so that you can select profiles from different images at the same time.
If the Spectral Profile Source Panel is not already visible, open it via .
Add another profile source relation with
and change the Source to the desired raster images.
If you now collect new spectral information, two profiles will appear in the same Spectral Library Window.
Tip
Change the color of one of the profile by changing the Style in the Spectral Profile Sources.
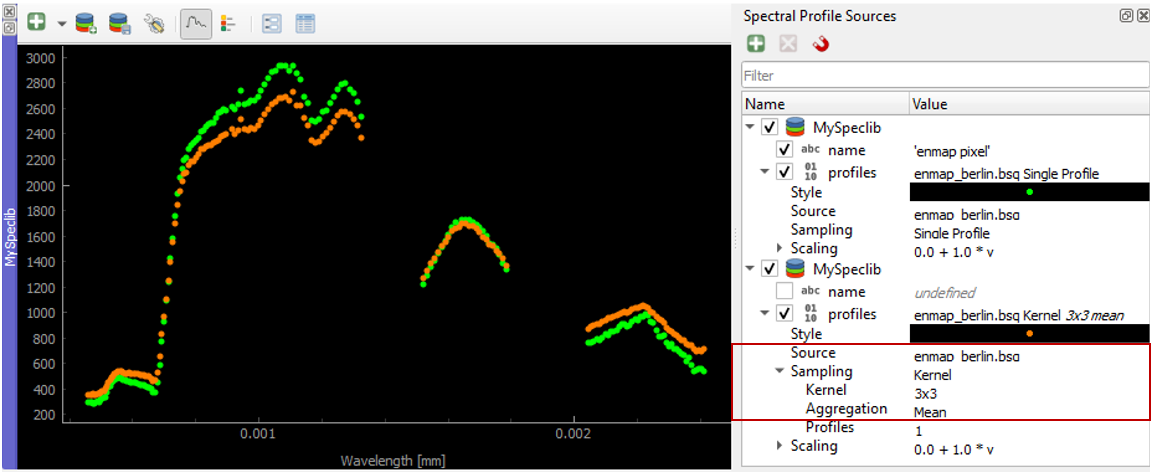
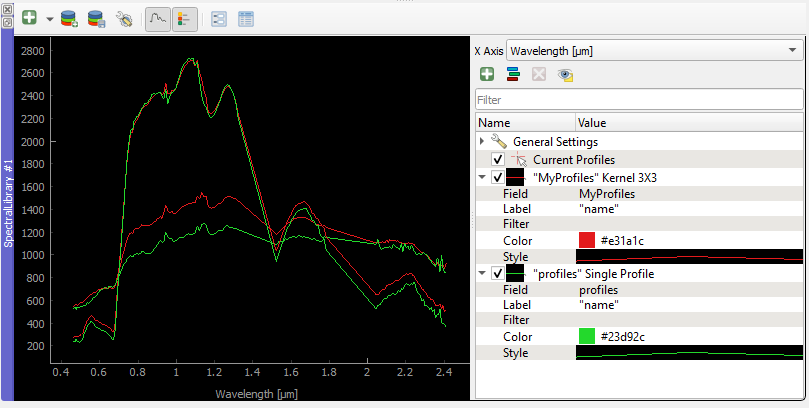
In a similar way you can compare profiles from the same raster image but using a different sampling methods.
In the second relation set the Source to the same image as the first relation.
Change the Sampling to e.g. a 3x3 Kernel mean profile.
Collect new pixel profiles.
Spectral Profile Sources Sampling Example
Adding information¶
The attribute table¶
You can also add more information to your spectral library by using the attribute table. Add additional fields to the table, e.g. in order to add information to every spectrum (id, name, classification label, …).
Now you can use the Add Field
dialog to add a new column.
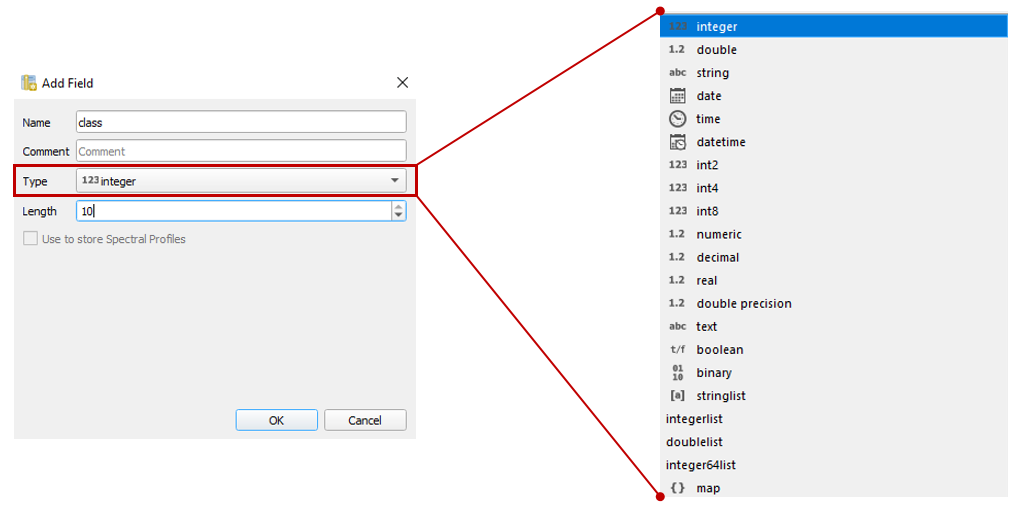
Select a data type of your choice.
A new column is added to the attribute table, which you can edit with a double click.
Tip
When you add a new attribute to the table, you can also choose to use it to store new spectral profiles by checking the Use to store spectral profiles checkbox. String, text and binary format can be used to store spectral profiles.
Add information in the layer properties window
It is also possible to add new information to the attribute table in the Layer Properties of the Spectral Library.
Navigate to the Fields tab and add a new field. Note: This view does not allow you to set the option Use to store spectral profiles.
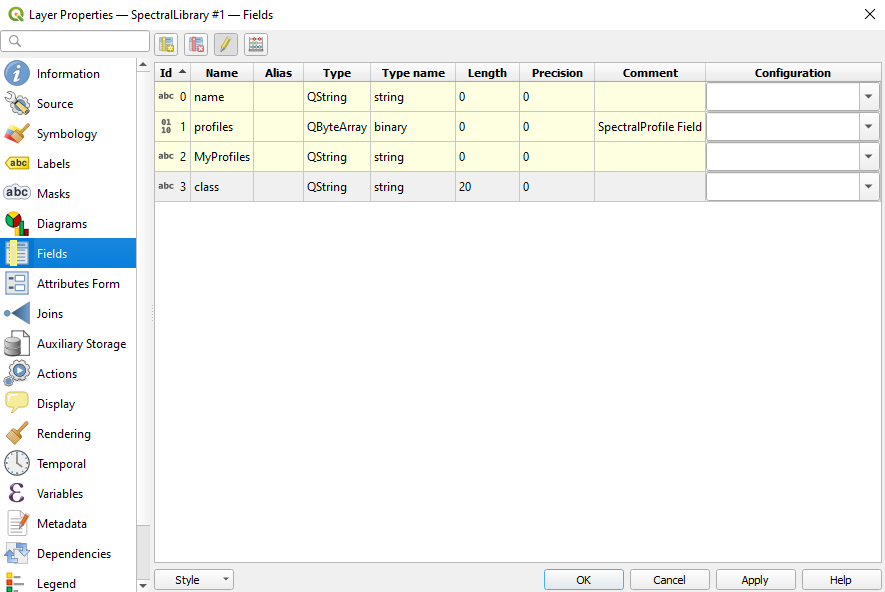
Overview of the Layer Properties / Fields section
In addition, the Layer Properties panel allows you to set a certain widget for a specific column.
Switch to the Attributes Form tab in the Layer Properties, select the desired column and choose a certain widget type, e.g. a default range, color, spectral profiles etc.
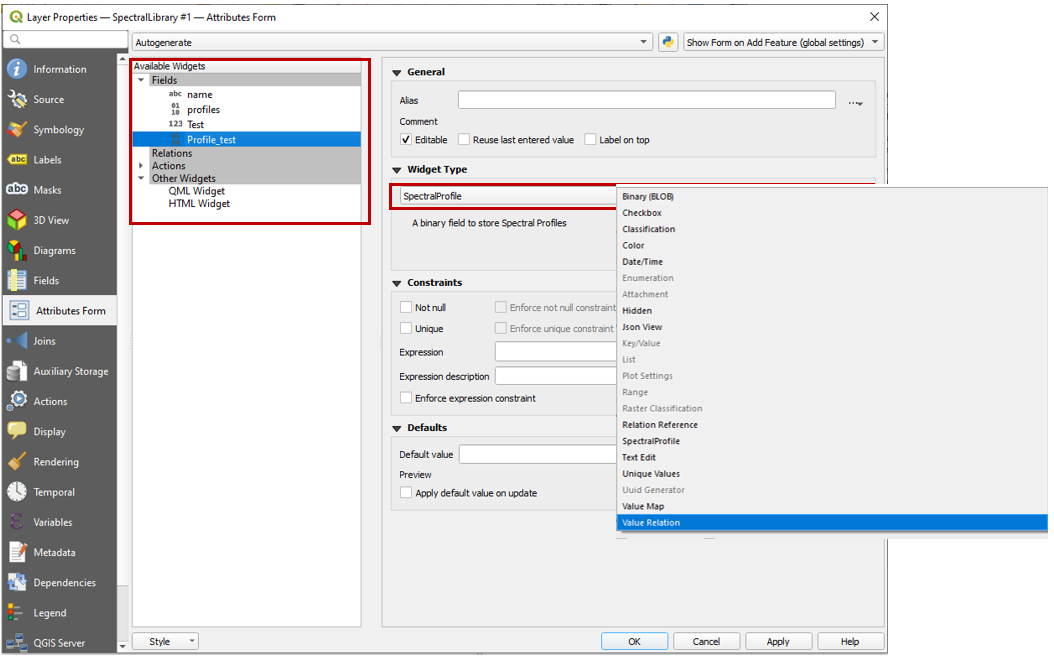
Selecting widget types for specific columns
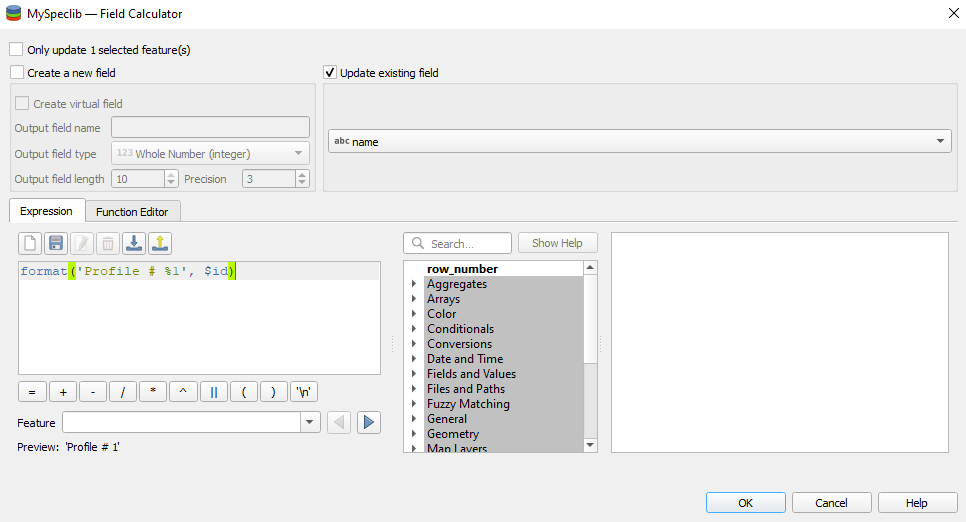
The field calculator
The field calculator allows you to modify or assess spectra and calculate new columns or modify existing ones using an expression.
Overview of the Field Calculator
Selecting spectra
Spectra can be selected in the attribute table and in the plot window itself. Selected spectra will be highlighted (blue background in the table; thicker line in a different color in the plot window).
Tip
You can inspect an individual value of a spectrum by holding the Alt key and clicking some position along the spectrum
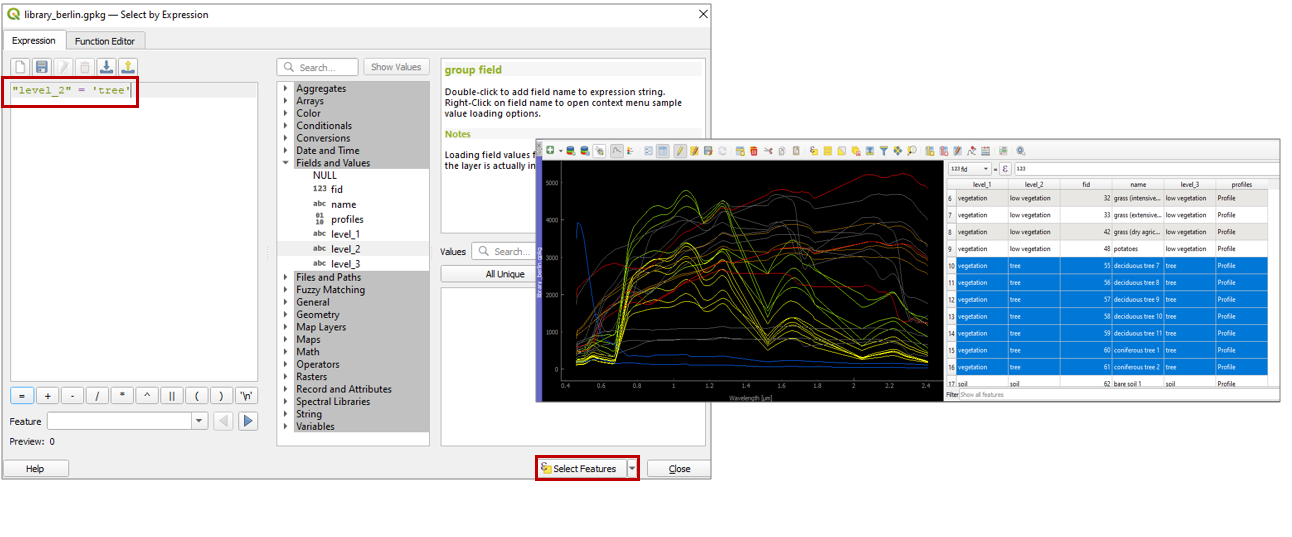
It is also possible to select and filter profiles with the common vector filter and selection tools, e.g. select spectra by expression:
Select profiles using an expression
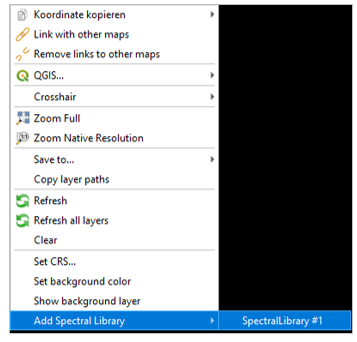
Show coordinates of profiles¶
Locations of spectra (if available) can be visualized as a point layer by right-clicking into the map window, and selecting Add Spectral Library > SpectralLibrary #
Advanced options¶
Create / Modify profiles with the Field Calculator¶
As already mentioned, the Field Calculator can modify attribute values of all or selected features. In addition, the field calculator can be used to calculate spectral profiles.
- Create a new Spectral Profile field based with Add Field
, use string, text or binary format and tick the Ise to store Spectral Profiles box.
- Open the field calculator
and search for spectralData or spectralMath in the Spectral Libraries tab.
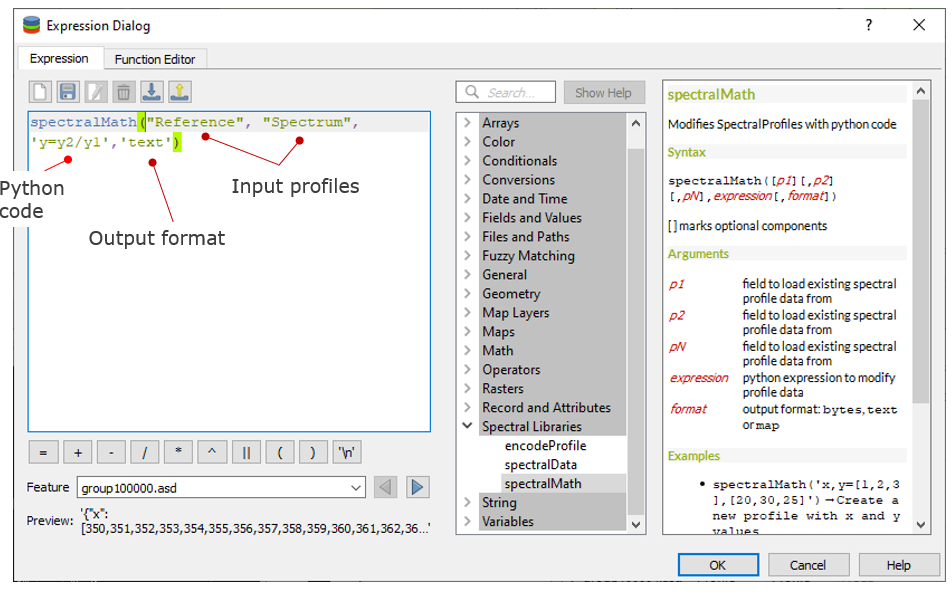
SpectralMath allows you to modify spectral profiles with Python code.
- To use the SpectralMath function, select a field from which to take the spectral profiles, define an expression and the format.
spectralMath("<profile field 1>", ..., "<profile field n>", '<python code>', '<output format>')
Note: The last argument defines the output format. It must correspond to the type you assigned when creating the new column.
Example of calculating new spectral profiles
SpectralData returns spectral profile values.
The following table shows some examples of how spectralMath and spectralData can be used.
| Description | Example |
|---|---|
| Multiply the existing profiles | spectralMath(“profiles”, ‘y *=2’, ‘text’) |
| Create a new profile with x and y values | spectralMath(‘x,y=[1,2,3],[20,30,25]’) |
| Return spectral profile values from map with spectral data from spectral profiles in field column “profiles” | spectralData(“profiles”) |
| Return xUnit string of the spectral profile e.g. ‘nm’ for wavelength unit | spectralData(“profiles”)[‘xUnit’] |
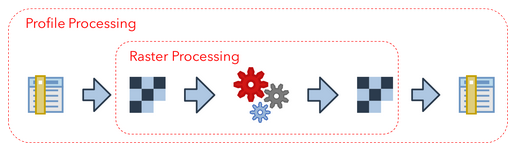
Spectral Processing¶
Overview of the spectral processing idea
The Spectral Processing framework allows you to use raster processing algorithms to create new profiles. Field values of your spectral library will be converted into artificial one-line raster images. In principally, this can be done with most of the field types:
| Field Type | Raster Size (band, height, n) | type |
|---|---|---|
| Spectral Profile | nb, 1, n | int/float |
| integer | 1, 1, n | integer |
| float | 1, 1, n | float |
| text | 1, 1, n | int (classification) |
These temporary raster images are input to standard QGIS processing algorithms or QGIS processing models. If they generate raster outputs, these outputs can be converted back into field values of the spectral library:
| Raster Output | Spectral library Field Type |
|---|---|
| (>1, 1, n) int/float | Spectral Profile |
| (1, 1, n) int | integer |
| (1, 1, n) float | float |
This allows you to use the same algorithms to modify spectral profiles as you may want to use to manipulate raster images. Furthermore, you can make use the QGIS model builder to create (potentially very large and complex) models and use them for both, spectral libraries and raster image processing.
To use the Spectral Processing tool open
and choose the desired algorithm, e.g. Spectral resampling.
Select the input profiles to be translated to the temporary raster layer and specify the outputs. Select an existing field or enter a name to create a new field.
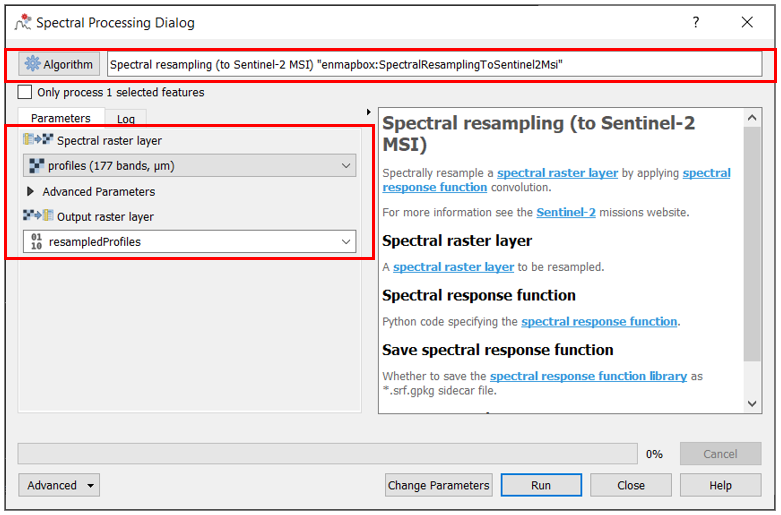
Spectral Processing Example
Visualization settings¶
General profile plot settings¶
The Profile Plot displays spectral profiles. Toggling the Profile View icon shows or hides the plot panel.
This can be useful, for example to enlarge the attribute table and focus on attribute modifications.
You can adjust the extent of the visualized data range and units
in the plot context menu
using the mouse cursor while keeping the right mouse button pressed
in the visualization settings view
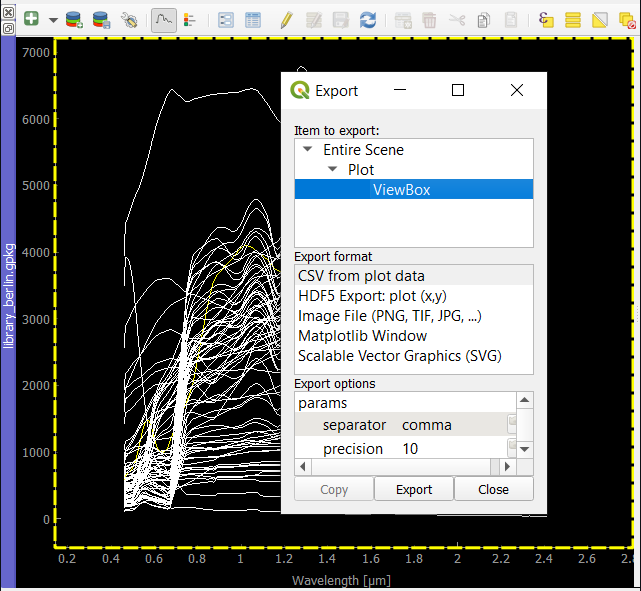
You can also export the entire plot scene or visible view box by clicking into the plot and select .
Export options of the spectral library
Visualizing profiles¶
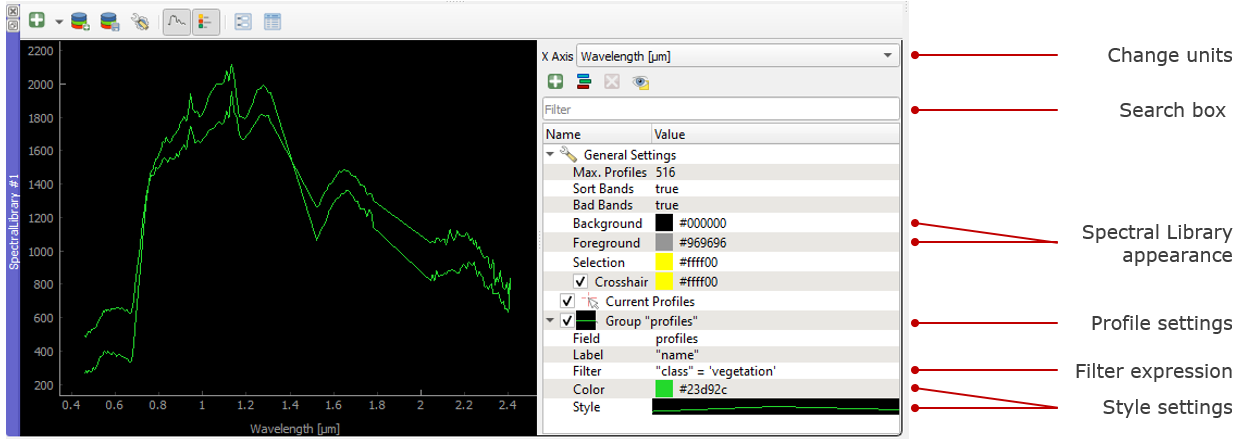
The visualization settings of the spectral library allow you to customize the view according to your needs. You can define multiple visualization groups that describe how profiles from a specific field and with specific attributes should be visualized.
Overview of the visualization settings in the Spectral Library window
It is also possible, to change the appearance of the Spectral Library window, i.e., bright or dark.
Moreover, activate or deactivate the crosshair and choose a color.
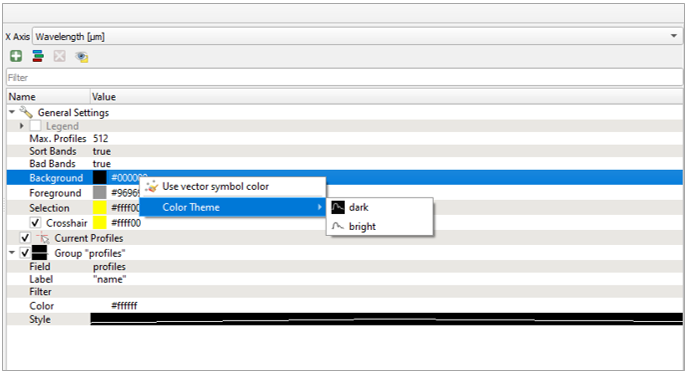
The Current Profiles section shows you all the spectra that have been collected but do not yet appear in the attribute table. Change the color and symbol, or add a line between the points by double clicking the profile below the Current Profile section and adjust the style settings.
Working with multiple visualization groups
The spectral library visualization settings also allow you to add several profile Groups with different style settings.
- Add a second visualization group with
.
- If you want rename Group “profiles”.
- Change the color for both groups in the Color.
- Under Field you can specify which spectral profile column of the attribute table you want to use.
If you have more than one column that stores spectral information, you can have different visualization groups using different profiles.
If you have only one column where spectral information is stored, but you have another column storing e.g. class names, you can use the Filter field to define an expression and select only specific class names, e.g. Impervious and Vegetation and visualize these profiles in different colors.
Colorize spectra by attribute¶
Spectra can be colorized according to their attributes, e.g. their class name.
In the Data Views panel on the left, right click
on the spectral library that we are currently using and select the Layer Properties.
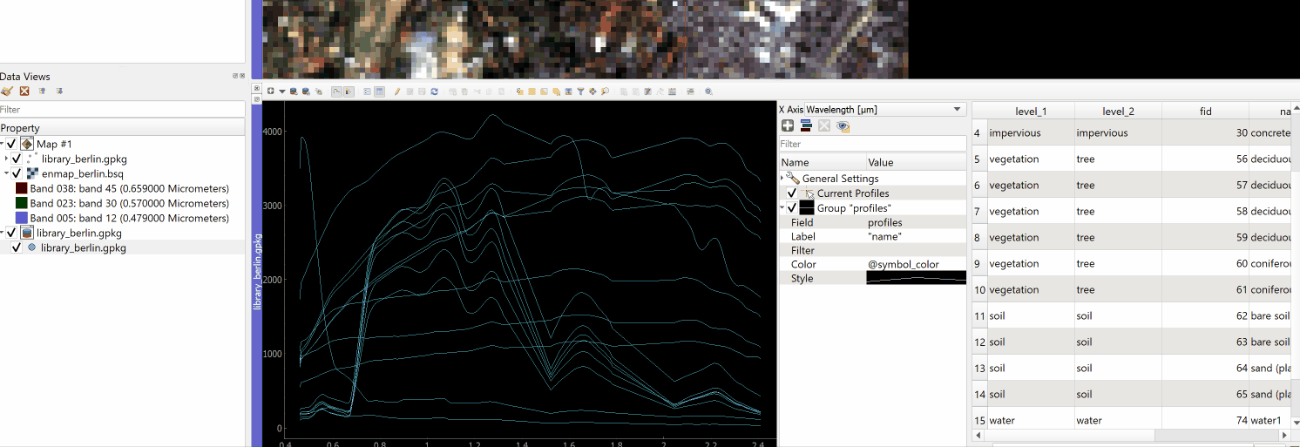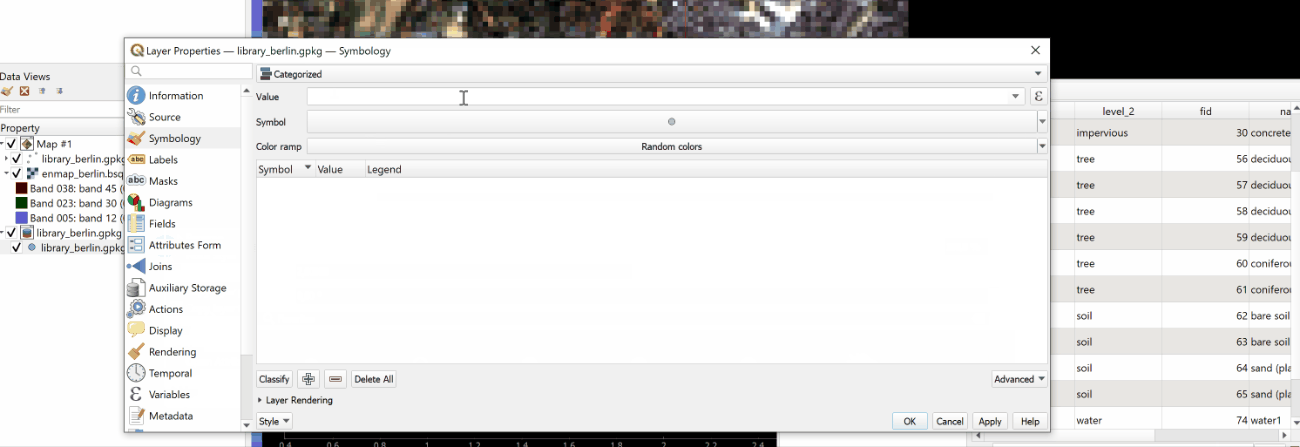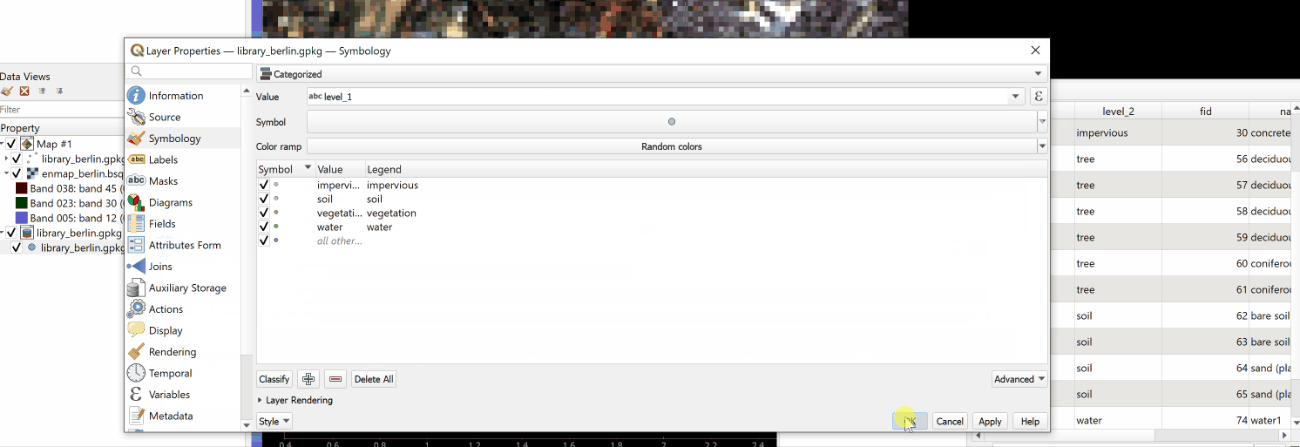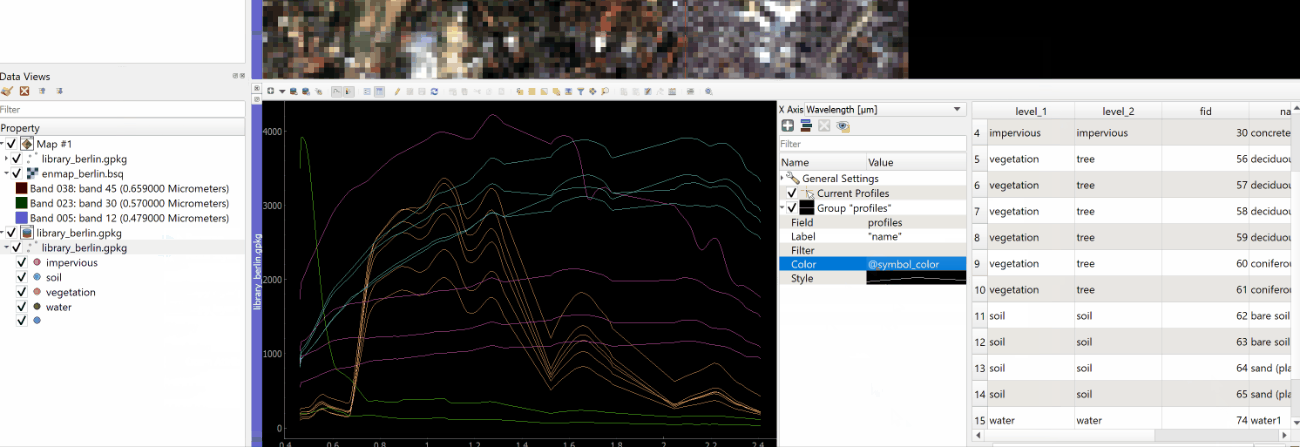
Switch to the Symbology
tab and select the Categorized renderer at the top.
In the Column droplist select the desired column and click Classify.
Confirm with Ok and close the window.
In the Spectral Library Window activate the visualization settings with the
button.
Loading, Saving and Importing / Exporting¶
Load and Save Spectral Libraries¶
Loading or Saving a spectral library means to load or save vector files.
Load any vector source in the Data Source Panel into a Spectral Library Viewer.
The vector layer does not need to contain any Spectral Profile fields. You can add or define them afterwards.
If your spectral library uses an in-memory vector layer backend, all data will be lost if the layer is closed. This is the case if the Spectral Library Viewer was opened from scratch with an empty spectral library. In this case, don’t forget to export collected profiles before closing the Spectral Library Viewer.
If your spectral library already uses a file backend (e.g. .gpkg, .geojson), Style and other layer specific information are not saved in the data source file, but the QGIS project or a QGIS specific sidecar .qml file.
Open to create or update the .qml file and ensure that the Spectral Profile fields will be restored when re-opening the data set.
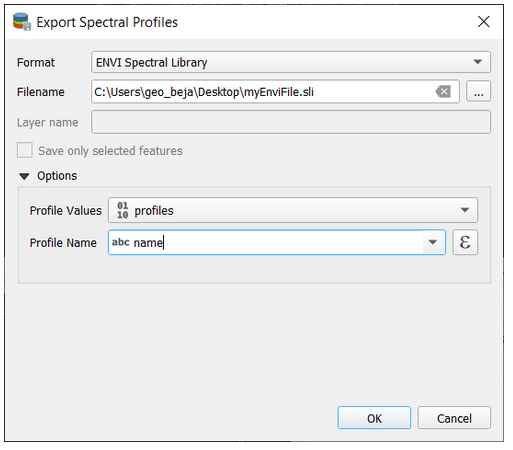
Exporting Profiles¶
The Export dialog allows you to export all or selected profiles as Geopackage (.gpkg), GeoJSON (.geoson) or ENVI Spectral Library (.sli).
The ENVI Spectral Library does not allow saving profiles with different spectral settings (number of bands, wavelength units, FWHM, …) in the same file. Therefore, you need to select one (out of multiple) profile fields. Profiles with different spectral settings will be exported into different ENVI files.
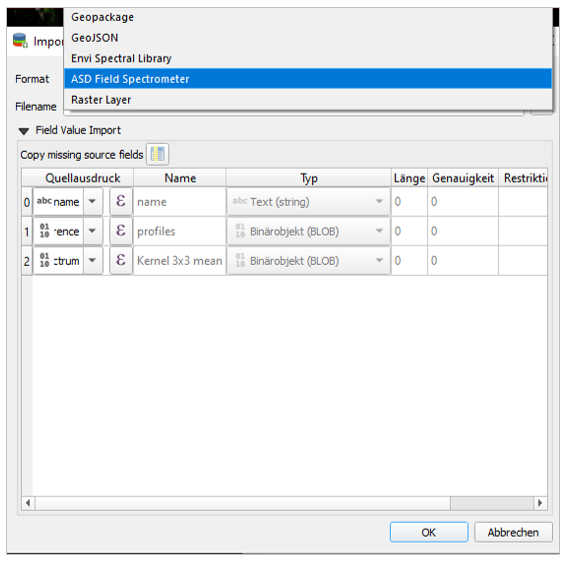
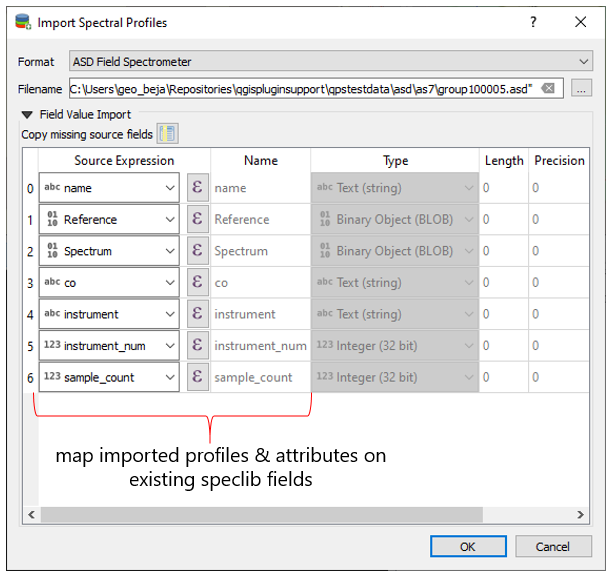
Importing Profiles¶
To import none-vector files into an existing spectral librar use the Import Spectral Library
button.
Possible formats to be imported: ENVI Spectral Library, Geopackage, ASD Field Spectrometer measurements, Raster Layer.
You can also import ASD Field Spectrometer measurements and map and modify the imported profiles and attributes accordingly.
Spectral Profile JSON format¶
The EnMAP-Box stores the minimum data to plot a single profile in a JSON object. In its most simple way, this JSON object contains a single array “y” of length n, with n = number of spectral profile values:
{
"y": [43, 23, 45, 63,45]
}
In this case it can be assumed that the corresponding ‘x’ values are an increasing band index “x”: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4].
The JSON object can describe the “x”, the axis units and a vector of bad band values explicitly:
| Member | Content |
|---|---|
| y | An array with n profile values |
| x | An array with n profile value locations |
| yUnit | String that describes the unit of y values |
| xUnit | String that describes the x value unit |
| bbl | A bad band list |
Other metadata to describe spectra profiles are stored in additional vector layer fields.
As JSON object, a single hyperspectral EnMAP profile may therefore look like:
{
"bbl":[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],
"x":[0.46,0.465,0.47,0.475,0.479,0.484,0.489,0.494,0.499,0.503,0.508,0.513,0.518,0.523,0.528,0.533,0.538,0.543,0.549,0.554,0.559,0.565,0.57,0.575,0.581,0.587,0.592,0.598,0.604,0.61,0.616,0.622,0.628,0.634,0.64,0.646,0.653,0.659,0.665,0.672,0.679,0.685,0.692,0.699,0.706,0.713,0.72,0.727,0.734,0.741,0.749,0.756,0.763,0.771,0.778,0.786,0.793,0.801,0.809,0.817,0.824,0.832,0.84,0.848,0.856,0.864,0.872,0.88,0.888,0.896,0.915,0.924,0.934,0.944,0.955,0.965,0.975,0.986,0.997,1.007,1.018,1.029,1.04,1.051,1.063,1.074,1.086,1.097,1.109,1.12,1.132,1.144,1.155,1.167,1.179,1.191,1.203,1.215,1.227,1.239,1.251,1.263,1.275,1.287,1.299,1.311,1.323,1.522,1.534,1.545,1.557,1.568,1.579,1.59,1.601,1.612,1.624,1.634,1.645,1.656,1.667,1.678,1.689,1.699,1.71,1.721,1.731,1.742,1.752,1.763,1.773,1.783,2.044,2.053,2.062,2.071,2.08,2.089,2.098,2.107,2.115,2.124,2.133,2.141,2.15,2.159,2.167,2.176,2.184,2.193,2.201,2.21,2.218,2.226,2.234,2.243,2.251,2.259,2.267,2.275,2.283,2.292,2.3,2.308,2.315,2.323,2.331,2.339,2.347,2.355,2.363,2.37,2.378,2.386,2.393,2.401,2.409],
"xUnit":"Micrometers",
"y":[405,397,412,410,402,413,421,427,444,446,445,445,476,491,495,504,504,519,532,530,536,539,533,527,529,527,529,526,530,524,520,521,522,523,507,514,505,502,494,497,543,603,703,769,845,930,1007,1096,1178,1249,1314,1359,1388,1386,1419,1432,1432,1435,1471,1498,1479,1487,1482,1499,1507,1517,1509,1534,1532,1507,1557,1527,1552,1605,1534,1555,1577,1564,1582,1600,1611,1643,1659,1678,1684,1672,1687,1659,1697,1624,1612,1602,1576,1515,1508,1513,1522,1542,1575,1602,1632,1649,1663,1639,1602,1587,1530,977,996,1026,1063,1086,1108,1123,1169,1177,1191,1194,1210,1222,1208,1201,1187,1182,1146,1157,1112,1093,1085,1096,1058,1041,754,781,804,796,780,792,812,825,851,803,812,836,834,818,823,842,842,860,851,880,844,856,847,846,819,842,820,754,768,731,728,750,695,735,675,718,640,601,684,744,635,568,696,637,592]}
}
Note that conceptually profile objects can differ in its wavelength etc.
Text View¶
Attribute Table View¶
Todo
…