Last Update: 2020-08-12
Installation
Overview
If you like to develop an EnMAP-Box application, or more general, a QGIS and Qt application, we recommend to use a state-of-the-art Integrated Development Environment (IDE) like PyCharm. It offers run-time debugging, code completion, spell-checking, syntax highlighting, SCM support, unit-testing and many other helpful things.
1. Have Git installed
If not, download and install Git from https://git-scm.com/downloads
Check if git is installed to your local shell, e.g. as:
C:\Windows\System32>git --version
git version 2.26.0.windows.1
2. Clone this repository
Clone the EnMAP-Box repository (or a fork) to your local my_repositories folder and update
its submodules by:
cd my_repositories
git clone --recurse-submodules git@github.com:EnMAP-Box/enmap-box.git
cd enmap-box
git config --local include.path ../.gitconfig
The last line ensures that pull requests will update submodules as well.
Now you can use git pull to update your local copy of the EnMAP-Box repository:
cd my_repositories/enmap-box
git pull
Tip
Replace the repo uri with that of your EnMAP-Box repo fork, if you like to provide code via pull requests.
3. Setup a QGIS environment
This section gives examples how you can setup a QGIS & EnMAP-Box development used by PyCharm on different platforms.
a) OSGeo4W (Windows)
1. Install or update packages
Install QGIS using the OSGeo4W Network installer https://qgis.org/en/site/forusers/download.html
Install the OSGeo4W environment to a folder of choice (preferably one you have permanent writing access to). In following this is called OSGeo4W.
Start the OSGeo4W Setup.
- Go forward to these steps by clicking next. Usually the default settings should be fine
‘Advanced Install’
‘Install from Internet’
‘Root Directory’ (should be your OSGEO4W directory)
Select Local Package Directory (default)
Select Your Internet Connect (default Direct Connection)
Choose A Download Site (default https://download.osgeo.org )
Select Packages to install / update
Package
Note
qgis
recent official QGIS version
python3-scikit-learn
Press Next to install packages / updates
2. Setup development environment
Copy the qgis-env.bat and start_pycharm.bat from https://github.com/EnMAP-Box/enmap-box/tree/main/.env/osgeo4w to a local folder, e.g. your windows desktop
Modify the qgis-env.bat config section to fit to your local environment, i.e. set the correct paths to your local OSGeoW installation and PyCharm executable
@echo off :: ### CONFIG SECTION ### :: root of local OSGEO4W installation set OSGEO4W_ROOT=D:\OSGeo4W :: PyCharm executable, adjust for version updates set PYCHARM_EXE="C:\Program Files (x86)\JetBrains\PyCharm 2022.1.2\bin\pycharm64.exe" :: git binaries and git lfs binaries set BIN_GIT=C:\Program Files\Git\bin set BIN_LFS=C:\Program Files\Git LFS
Call start_pycharm.bat to open PyCharm within the latest QGIS release. You can modify the start script to start a different QGIS build. E.g.
call "%~dp0\qgis-env.bat" qgis-ltr start "PYCHARM" /B %PYCHARM_EXE%
will start the QGIS Long Term Release (if installed) instead of the latest QGIS release (qgis).
Possible QGIS versions provided by the OSGeo4W installer are:
Build
Description
qgis
QGIS Desktop (latest release)
qgis-ltr
QGIS Desktop (long term release)
qgis-dev
QGIS nightly build of the development branch
qgis-rel-dev
QGIS nightly build of the latest release branch
b) Linux
Install QGI as described in https://qgis.org/en/site/forusers/download.html
c) macOS
Install QGIS as described in https://qgis.org/en/site/forusers/download.html
d) Docker
tbd.
e) Setup Conda (all platforms)
Warning
Installing QGIS via conda is not officially supported by the QGIS core development team. The QGIS versions available in conda can therefore differ from the official QGIS versions!
The installation of QGIS within a conda / anaconda environment is (almost) the same on macOS, windows or linux. Using conda it is often much easier to install additional python packages while admin rights are not required.`
Make sure conda is installed on your system.
Create a new conda environment named qgis_stable as specified in conda_environment.yml:
conda env create --name qgis_stable --file https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EnMAP-Box/enmap-box/main/conda_environment.yml
Tip
Depending on the components and applications you like to use, it might be required to install more packages.
If you cloned the EnMAP-Box repository you can also point to the local conda_environment.yml.
Edit the --name or the YAML file itself as you wish. For more information on creating and managing conda environments visit the conda documentation
Activate the new environment
conda activate qgis_stable
Now you can start `QGIS`_, the Qt Designer and Qt Assistant from your conda shell:
qgis designer assistant
To easily start applications like PyCharm in this environment, which have not been installed by conda, you might define an alias during the activation of the environment.
Create an activation script and define an alias for PyCharm:
Windows: <your conda installation>/envs/qgis_stable/etc/conda/activate.d/pycharm-activate.bat
@echo off doskey pycharm="<path to pycharm executable>"
MacOS: <your conda installation>/envs/qgis_stable/etc.conda/activate.d/pycharm-activate.sh
alias pycharm='open -a PyCharm\ CE.app'
For completeness, also create a deactivation script:
Windows: <your conda installation>/envs/qgis_stable/etc/conda/deactivate.d/others-deactivate.bat
@echo off doskey pycharm=
MacOS/Linux: <your conda installation>/envs/qgis_stable/etc.conda/deactivate.d/pycharm-deactivate.sh
alias pycharm=
f) Setup Mambaforge (all platforms)
Mambaforge is a reimplementation of Conda and behaves very similar. Make sure to read and understand the previous section explaining Conda, before using Mambaforge.
Execute one of the following installation command inside your Mambaforge/Miniforge prompt:
QGIS Long Term Release (LTR) environment:
mamba env create -n enmapbox_long_term -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EnMAP-Box/enmap-box/main/.env/conda/enmapbox_full_longterm.yml
QGIS Latest Release (LR) environment:
mamba env create -n enmapbox_full_latest -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EnMAP-Box/enmap-box/main/.env/conda/enmapbox_full_latest.yml
For additional reading on Mambaforge see: https://mamba.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
4. Setup PyCharm
Start PyCharm and add my_repositories/enmap-box as new project via File > Open File or Project
If this is not already the case, tell PyCharm where to find your Git-executable. Open File > Settings > Version Control > Git to set Path to Git executable. Press Test to check the used Git version.
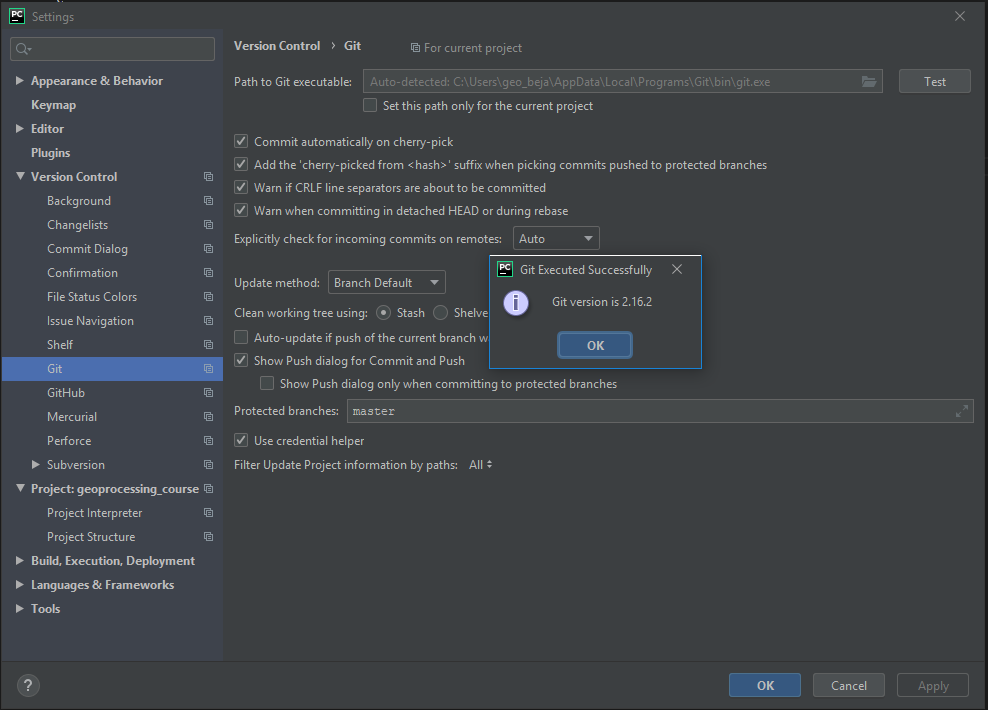
Fig. 30 Set the Git executable used by PyCharm
Tip
Use
whereto return the path of a git-executable that is available in your DOS/Linux/macOS shell(qgis_stable) C:\>where git C:\Users\geo_beja\AppData\Local\Programs\Git\cmd\git.exe
Switch to Project: enmap-box > Project Interpreter and select the QGIS python as python interpreter.
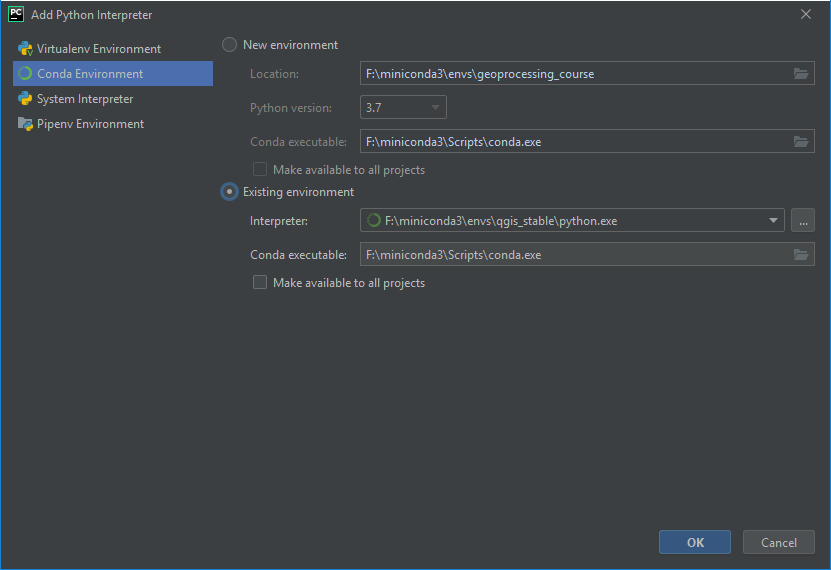
Fig. 31 Add the qgis_stable python to the list of python interpreters
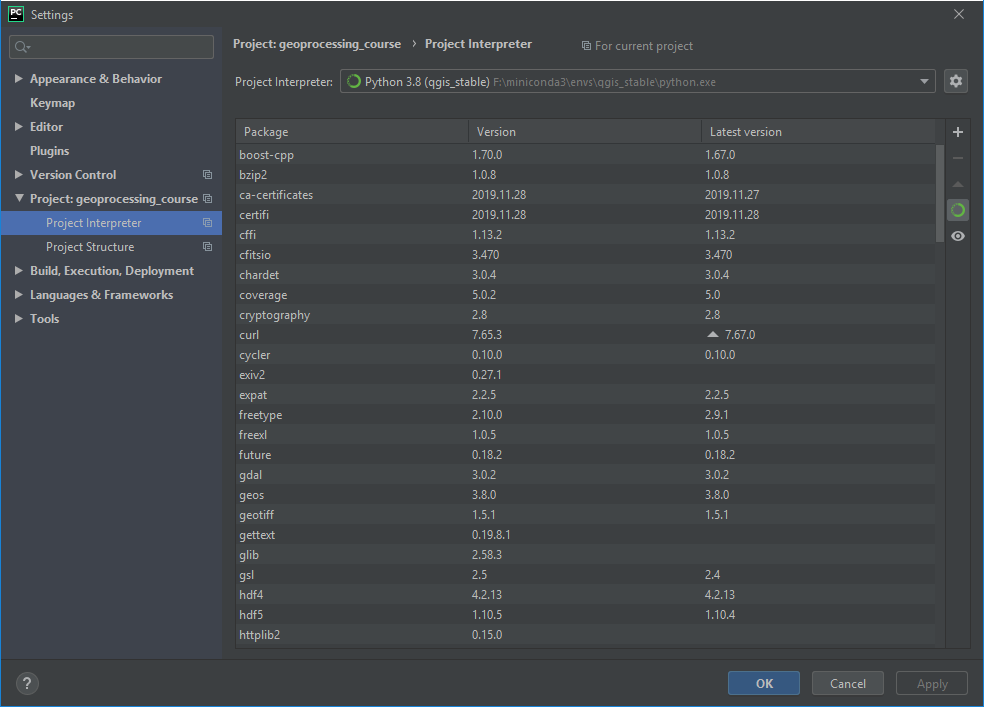
Fig. 32 Select the qgis_stable python as project interpreter
Switch to Project Structure and add the QGIS python folder as additional project content root.
OSGeo4W
<your OSGeo4W folder>\bin\pythonLinux
/usr/bin/python3macOS
/Application/QGIS.app/Contents/MacOS/bin/python3conda (win)
<your conda installation>/envs/qgis_stable/Library/pythonconda (linux)
<your conda installation>/envs/qgis_stable/share/qgis/pythonconda (macOS)
<your conda installation>/envs/qgis_stable/QGIS.app/Contents/MacOS/../Resources/pythonRight-click on the
pluginssubfolder and select Sources. This makes QGIS internal plugins like the “processing” plugin available to PyCharm.Now the PyQGIS API is available to your Python installation.
Tip
The same way allows you to include other directories to your project’s PYTHONPATH, e.g. to make code available from other folder or repositories.
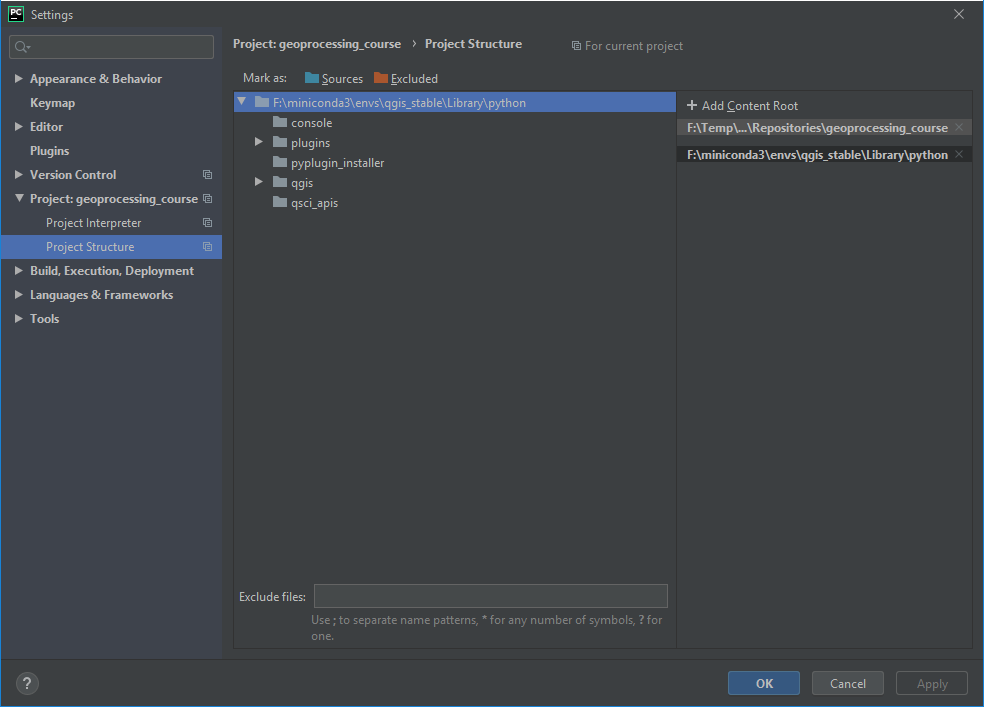
Fig. 33 Use
qgis_stable/Library/pythonas additional content rootPyCharm and PyQGIS may need the environmental variable
QGIS_PREFIX_PATH. Typical paths are:QGIS Installation
QGIS_PREFIX_PATH
OSGeo4W
<OSGeo4W>/apps/qgis
Linux
conda (Windows)
<conda installation>\envs\qgis_stable\Library
conda (Linux)
<conda installation>/envs/qgis_stable
conda (macOS)
<conda installation>/envs/qgis_stable/QGIS.app/Contents/Resources
If not already set in the environment from which you started PyCharm, you can set it explicitly. Open Run > Debug … > Edit Configurations and add the QGIS_PREFIX_PATH to the User environmental variables. This way PyCharm runs python files in a environment with QGIS_PREFIX_PATH defined.
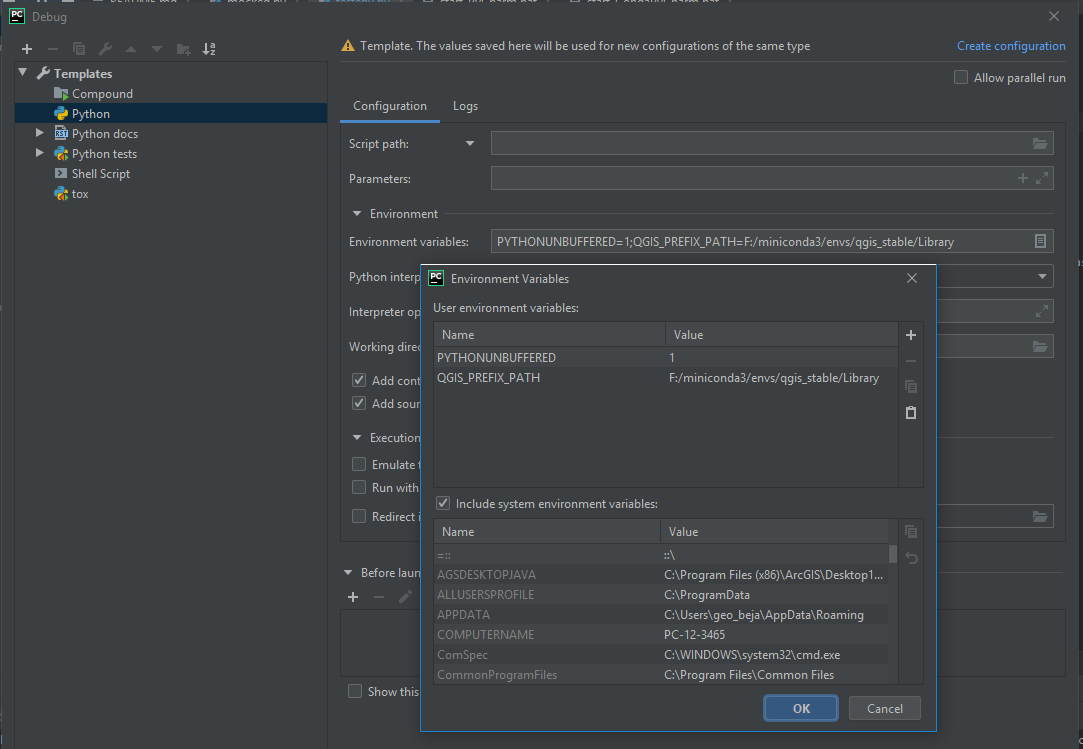
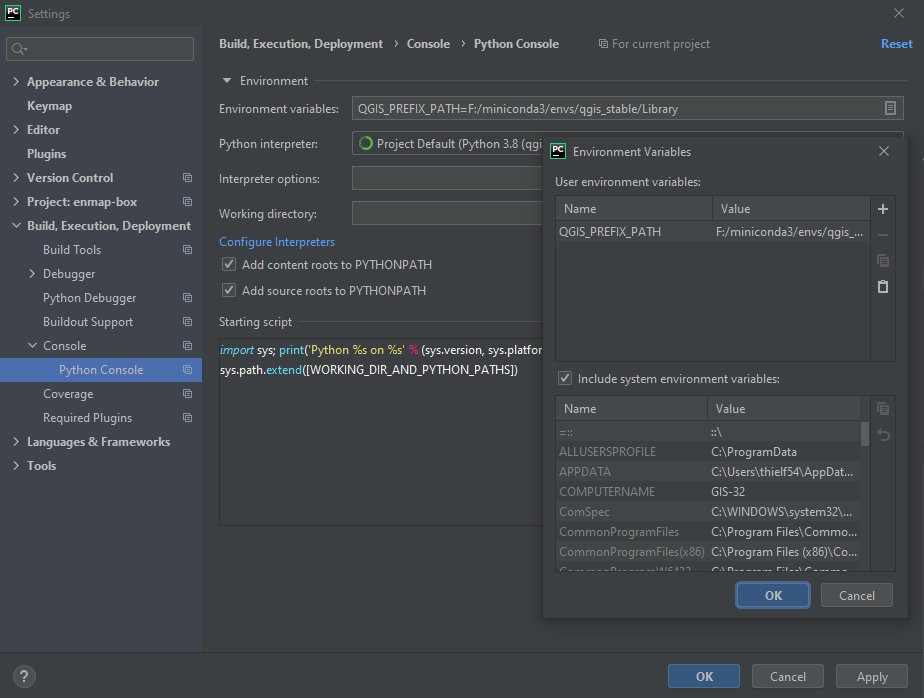
Also define the Environment variables for the Python console. Go to File > Settings > Build, Execution, Deployment > Console > Python Console and add QGIS_PREFIX_PATH to the Environment variables.
You may also modify the shell used in your PyCharm terminal to use the QGIS environment. Open Tools > Terminal and set the shell path to, for example:
QGIS Installation
Terminal path
OSGeo4W
cmd.exe "/K" qgis_env.bat(see above how to create theqgis_env.bat)conda (Windows)
cmd.exe "/K" <conda installation>\Scripts\activate.bat qgis_stable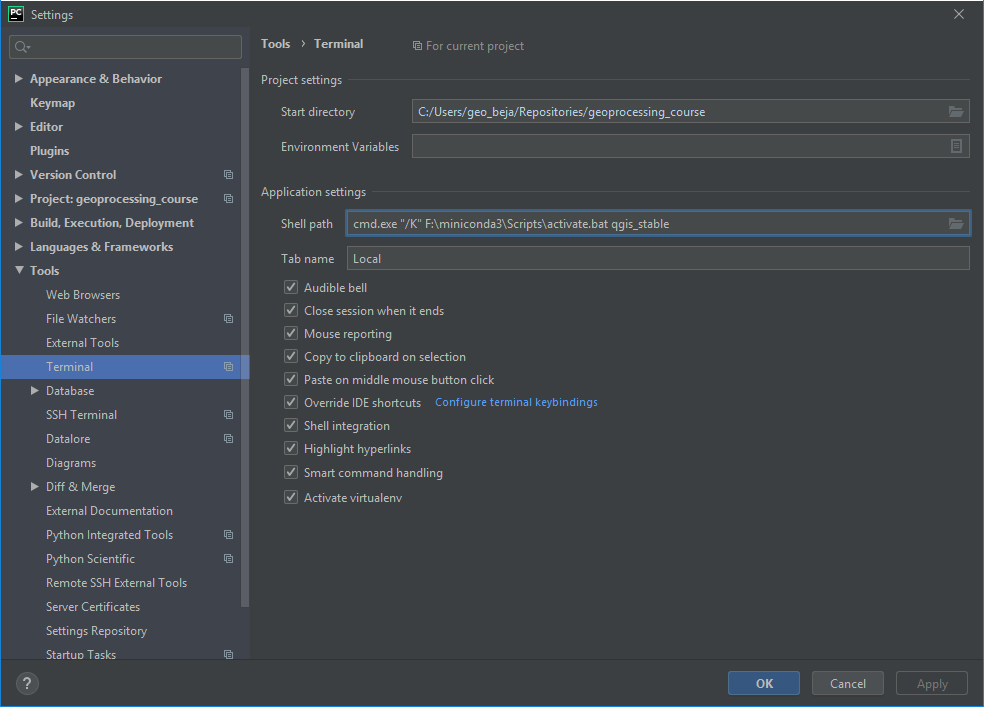
Fig. 34 How to use the conda terminal in PyCharm
Test the Python environment
To check if the QGIS API is available, open a Python Console and import the QgsApplication object.
from qgis.core import QgsApplication QgsApplication.instance() is None
The output should return
True, as we have not initialized any QgsApplication.Now check if we can use the EnMAP-Box API to start the EnMAP-Box
import enmapbox enmapbox.run()
This should initialize a new QgsApplication and start the EnMAP-Box. The outputs printed to the python shell should look like:
Application state: QGIS_PREFIX_PATH env var: D:\miniconda3\envs\qgis_stable\Library Prefix: D:\miniconda3\envs\qgis_stable\Library Plugin Path: D:\miniconda3\envs\qgis_stable\Library/plugins Package Data Path: D:\miniconda3\envs\qgis_stable\Library/. Active Theme Name: Active Theme Path: D:\miniconda3\envs\qgis_stable\Library/./resources/themes\\icons/ Default Theme Path: :/images/themes/default/ SVG Search Paths: D:\miniconda3\envs\qgis_stable\Library/./svg/ C:\Users\geo_beja\AppData\Local\Temp\QGIS-PythonTestConfigPathp1k7w_s_\profiles\default/svg/ User DB Path: D:\miniconda3\envs\qgis_stable\Library/./resources/qgis.db Auth DB Path: C:\Users\geo_beja\AppData\Local\Temp\QGIS-PythonTestConfigPathp1k7w_s_\profiles\default/qgis-auth.db
If the terminal environment was setup well, you can start the EnMAP-Box from the Terminal window as well by
(qgis_stable) ..\enmap-box>python enmapbox
Other Tools
The Qt company provides several tools to that help to create Qt applications and are useful for PyQt and PyQGIS users as well.
Qt Assistant
The Qt Assistant allows you to browse fast and offline through Qt help files (*.qch). These files exists for
all Qt classes and the QGIS API. They can be generated event with Sphinx, which allows you to provide your
own source-code documentation as .qch file as well.
Start the Qt Assistant, e.g. from your PyCharm terminal:
(qgis_stable) $>assistant
Download the
*.qch*files which contain:the Qt API documentation files: https://github.com/PierreRaybaut/PyQtdoc
the QGIS API documentation qgis.qch
Go to Preferences > Add and add the following
*.qchfilesFile
Documentation
qgis.qch
qgis.core, qgis.gui
qtcore.qch
Qt5.QtCore
qtgui.qch
Qt5.QtGui
qtwidgets.qch
Qt5.QtWidgets
Now you can explore the Qt (
Q...) and QGIS (Qgs...) classes
Qt Designer
The Qt Designer is a powerful tool to create GUI frontends by drawing, drag and drop.
Created GUI form files are saved in a XML file ending with *.ui. These can be called from
python to automatically create the entire GUI backend, e.g. windows and buttons defined with the Qt Designer.
You can start the Qt Designer from your PyCharm terminal by:
(qgis_stable) $>designer
Fig. 35 Qt Designer showing the metadataeditor.ui for the Metadata editor.
Qt Creator
Qt Creator is the one-in-all IDE to develop Qt C++ applications. It includes the functionality covered by Qt Assistant (here called Help) and Qt Designer (here called form designer) and helps to browse C++ code. It is the preferred tool to explore the QGIS C++ source code, for example if you like to better understand what it does behind the QGIS python API.
Qt and the Qt Creator are available at https://www.qt.io/download. Ensure to install the code documentation for the same Qt version used by QGIS.
Fig. 36 Qt Creator with opened metadataeditor.ui.
OSGeo4W for Devs
If you work on windows and want to test your code based on nightly builds of the upcoming QGIS version, or like to inspect/debug the QGIS C++ API at runtime, you might use the OSGeo4W installer to setup your development environment:
Setup Environment
Download the (new) OSGeo4W installer (osgeo4w-setup.exe from https://www.qgis.org/en/site/forusers/download.html )
Install the nightly build branch qgis-dev and related debug symbols qgis-dev-pdb.
Install other required packages, e.g. pip3 etc. Later on. In case of missing packages, search and install via OSGeo4W installer first. If not available there, use the OSGeo4W shell and call pip.
Create a qgis-dev-env.bat to setup your QGIS environment
set OSGEO4W_ROOT=D:\OSGeo4W set QGISDISTR=qgis-dev set DIR_GIT=C:\Program Files\Git\cmd set DIR_LFS=C:\Program Files\Git LFS :: add GIT and LFS to path call "%OSGEO4W_ROOT%\bin\o4w_env.bat" path %OSGEO4W_ROOT%\apps\%QGISDISTR%\bin;%DIR_GIT%;%DIR_LFS%;%PATH% set QGIS_PREFIX_PATH=%OSGEO4W_ROOT:\=/%/apps/%QGISDISTR% set GDAL_FILENAME_IS_UTF8=YES rem Set VSI cache to be used as buffer, see #6448 set VSI_CACHE=TRUE set VSI_CACHE_SIZE=1000000 set QT_PLUGIN_PATH=%OSGEO4W_ROOT%\apps\%QGISDISTR%\qtplugins;%OSGEO4W_ROOT%\apps\qt5\plugins set PYTHONPATH=%OSGEO4W_ROOT%\apps\%QGISDISTR%\python;%OSGEO4W_ROOT%\apps\%QGISDISTR%\python\plugins;%PYTHONPATH%
Don’t forget to make git and git-lfs available in this environment.
Create a qgis-dev-pycharm.bat in the same folder as qgis-dev.bat that starts PyCharm
call "%~dp0\QGIS-dev.bat" set PYCHARM_EXE="C:\Program Files (x86)\JetBrains\PyCharm 2020.3.4\bin\pycharm64.exe" start "PYCHARM" /B %PYCHARM_EXE% :: uncomment to start QGIS :: start "QGIS" /B "%OSGEO4W_ROOT%\bin%QGISDISTR%-bin.exe" %*
Call qgis-dev-pycharm.bat to start PyCharm and set your project settings to:
Project Interpreter: <OSGEO4W>binpython.exe
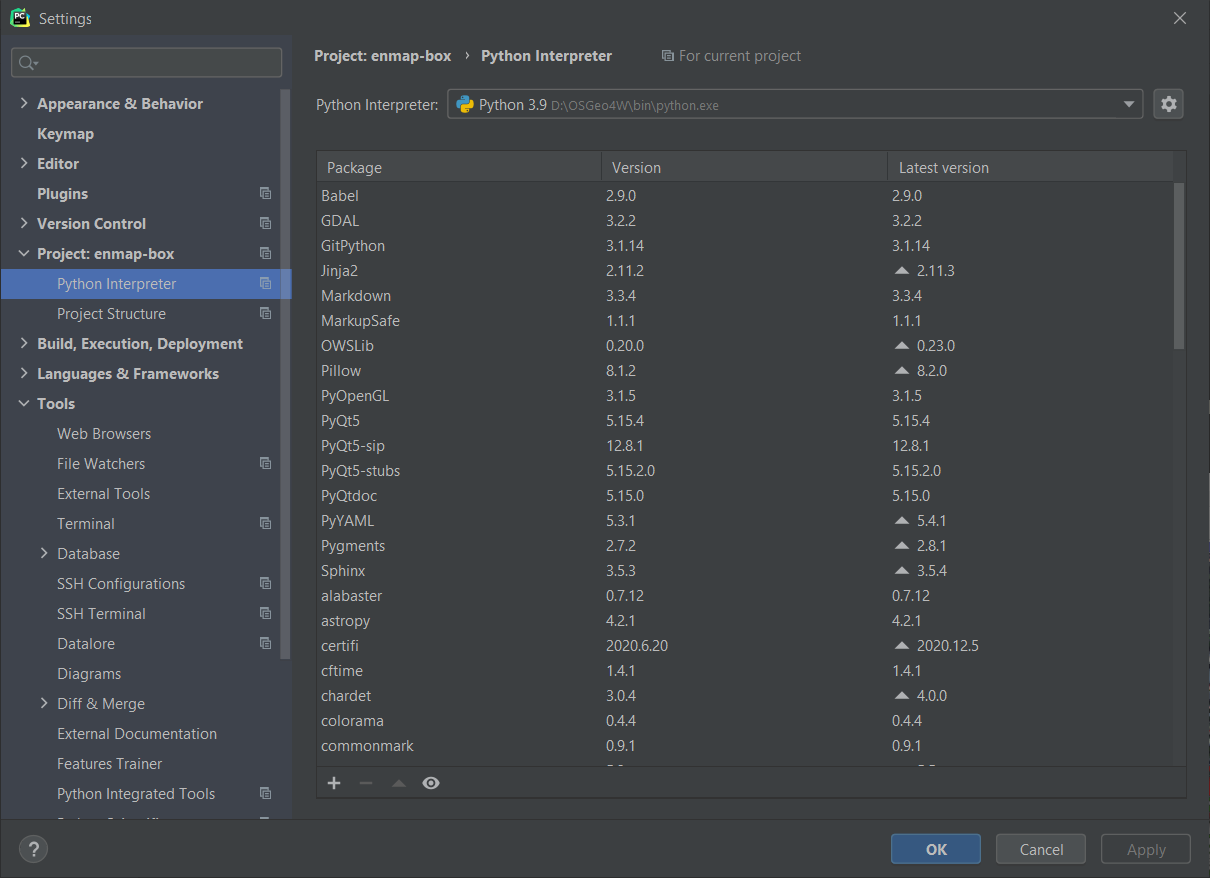
Fig. 37 Using the OSGeo4W python as project interpreter.
Terminal Shell Path: cmd.exe “/K” <your path to>qgis-dev.bat (this is why we created two batch files. qgis-dev.bat setups the environment, but does not start any app)
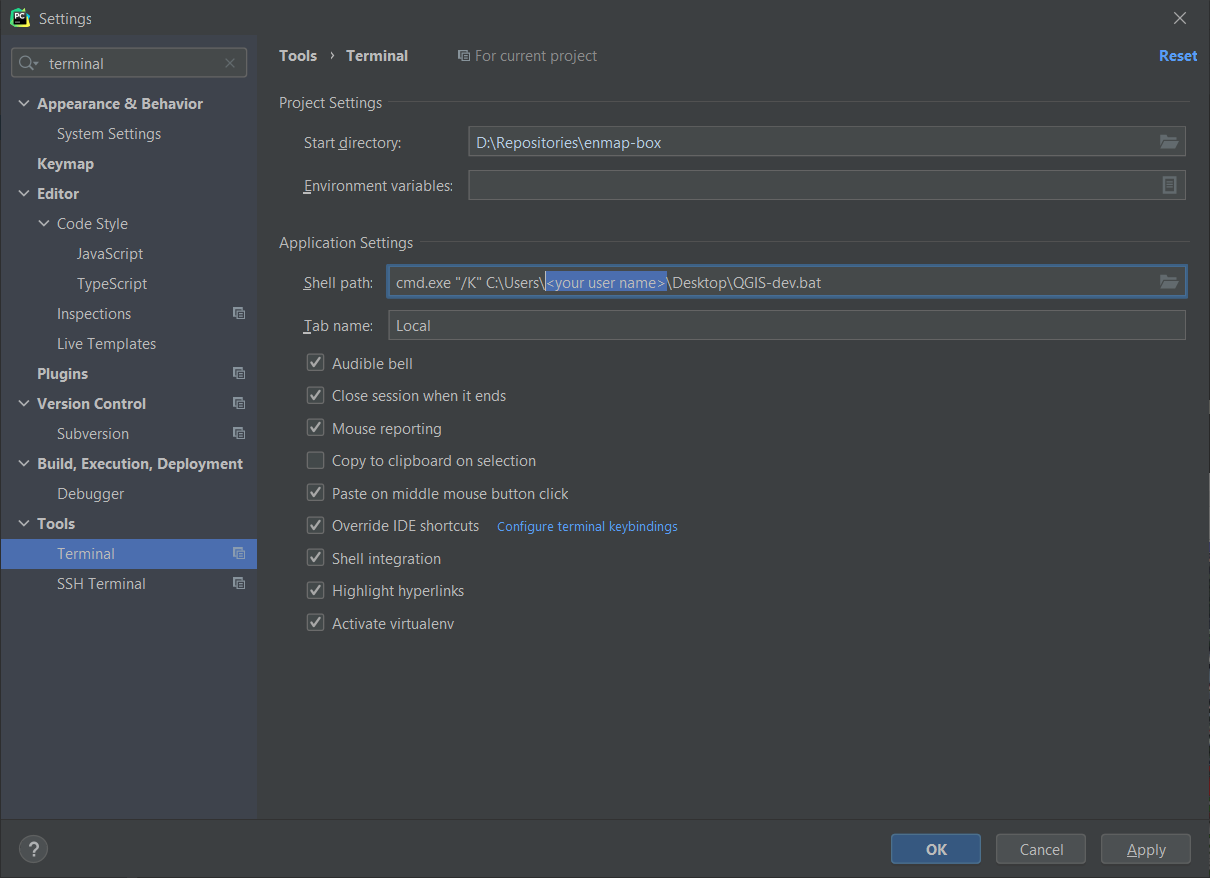
Fig. 38 The qgis-dev.bat will be called when starting the terminal
add <OSGEO4W>appsqgis-devpython and <OSGEO4W>appsqgis-devpythonplugins as source folders
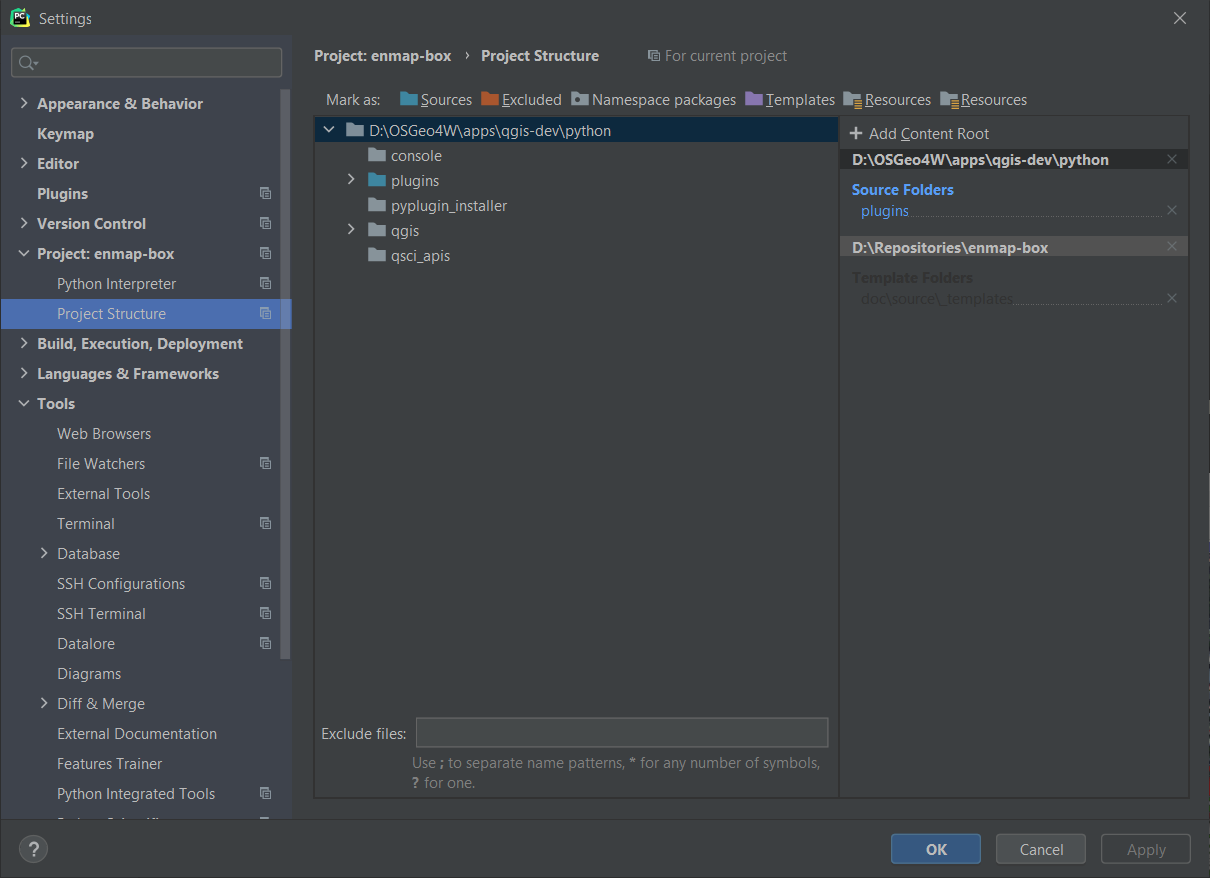
Fig. 39 Adding the QGIS python and pythonplugins folder as content roots.
Debug QGIS with Visual Studio
Clone the QGIS repo and checkout the latest master
Install Visual Studio and open the QGIS repo
Start a QGIS desktop, e.g. with qgis-dev from the OSGeo4W shell
Attach the Visual Studio debugger to a QGIS desktop instance
Open Debug > Attach to Process (CTRL+ALT+P)
Filter available processes by ‘QGIS’ and, e.g., select qgis-dev-bin.exe
Press the Attach button
References
Git -the simple guide (no deep shit) https://rogerdudler.github.io/git-guide/
Qt5 C++ API https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/
QGIS C++ API https://api.qgis.org/api/
QGIS Python https://qgis.org/pyqgis
QGIS Python developer cookbook https://docs.qgis.org/3.4/en/docs/pyqgis_developer_cookbook