Fit MeanShift
Mean shift clustering using a flat kernel. Mean shift clustering aims to discover “blobs” in a smooth density of samples. It is a centroid-based algorithm, which works by updating candidates for centroids to be the mean of the points within a given region. These candidates are then filtered in a post-processing stage to eliminate near-duplicates to form the final set of centroids. Seeding is performed using a binning technique for scalability.
Usage:
Open the algorithm from the processing toolbox.
Load an existing training dataset or create one by clicking the processing algorithm icon, then click run.
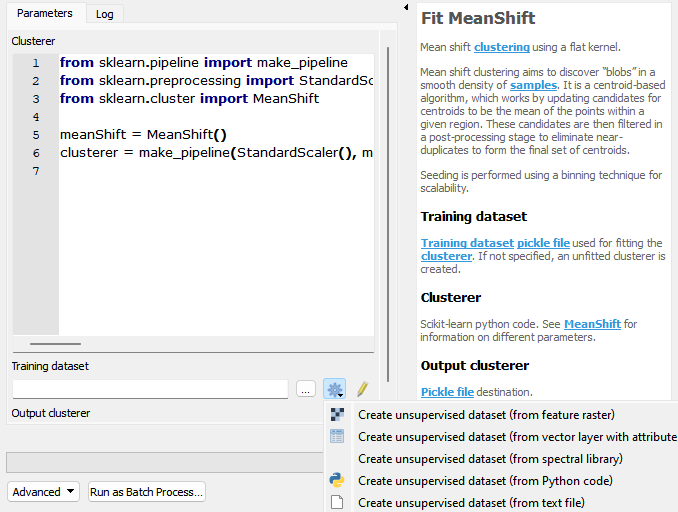
Parameters
- Clusterer [string]
Scikit-learn python code. See MeanShift for information on different parameters.
Default:
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler from sklearn.cluster import MeanShift meanShift = MeanShift() clusterer = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), meanShift)
- Training dataset [file]
Training dataset pickle file used for fitting the clusterer. If not specified, an unfitted clusterer is created.
Outputs
- Output clusterer [fileDestination]
Pickle file destination.
Command-line usage
>qgis_process help enmapbox:FitMeanshift:
----------------
Arguments
----------------
clusterer: Clusterer
Default value: from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.cluster import MeanShift
meanShift = MeanShift()
clusterer = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), meanShift)
Argument type: string
Acceptable values:
- String value
- field:FIELD_NAME to use a data defined value taken from the FIELD_NAME field
- expression:SOME EXPRESSION to use a data defined value calculated using a custom QGIS expression
dataset: Training dataset
Argument type: file
Acceptable values:
- Path to a file
outputClusterer: Output clusterer
Argument type: fileDestination
Acceptable values:
- Path for new file
----------------
Outputs
----------------
outputClusterer: <outputFile>
Output clusterer